. WOMEN’S EQUALITY . .
An article by Behrooz Ghamari Tabrizi in Counterpunch
Let me start with a straightforward proposition that is everywhere on social and mass media these days: The Islamic Republic’s patriarchal repression of women reached a tipping point after the murder in custody of Mahsa (Zhina) Amini by the Guidance Patrol on September 16, 2022. A revolt, led by young women, engulfed the entire country under the banner of women, life, freedom. At the root of this movement is the anti-women core of the Islamic regime and the struggle of Iranian women against it since its very beginning in 1979.
The whole nation — inside and outside the country, the global community, the progressive Left as well as the hawkish Right, stand in solidarity with this movement. The protests that began against the compulsory hijab and the demand for abolishment of the Guidance Patrol, has now become a full-fledged intersectional revolt for regime change in Iran, led by women.
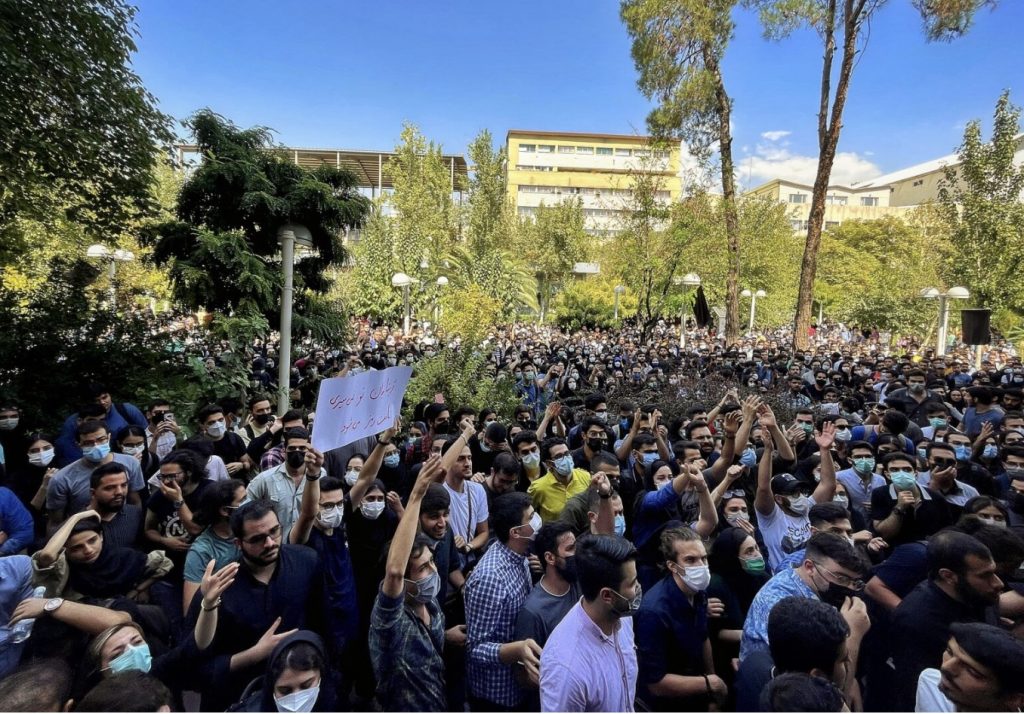

This indeed is true that the Islamic Republic instituted draconian patriarchal policies after the revolution on 1979 that stripped the very basic formal rights that women had been granted under the ancien régime. These measures formally reduced women to second-class citizens in matters of marriage, custody, inheritance, crime and judiciary, dress code, segregation, and many other spheres of social life. Yet, despite all this, women’s social mobility and presence in public sphere grew exponentially in the past four decades. Ironically, this is in part an effect of the unintended consequences of these policies. Women learned very quickly how to navigate the new terrain, push the boundaries of the new institutions, and in practice gain access to rights and privileges from which the Islamic Republic deprived them. The recent revolt could not materialize without the remarkable agentive presence and mobility of women who carved out a space for ceaseless social and political engagement during the past four decades. Women are revolting because they refuse to continue the struggle in a field the boundaries of which are drawn in the dilapidated spirits of patriarchy. Their gains have reached a hard as well as a glass ceiling that needs to be overcome.
The Iranian revolution succeeded in ending the monarchy on February 11, 1979. On February 26, only two weeks after the victory of the revolution, Ayatollah Khomeini annulled the Family Protection Law of 1967 and its 1975 amended version, which had given women more rights in divorce and matters of custody under the Shah. Since its inception, the clergy by and large had opposed the law’s basic premises, which they believed violated the Islamic views on women’s role in family. Khomeini knew that the unity and uniformity that his leadership afforded the revolutionary movement would not remain uncontested for long after the triumph of the revolution. He knew that the spirit of Islam and the symbolic revolutionary language with which it inspired millions of Iranians of many creeds and classes needed to be translated into a body of institutional projects of postrevolutionary state-building. So, he seized the opportunity to put women under the control of their menfolk.
Despite such overt assaults on women’s rights, most political parties continue to address women’s issues in the frame of revolutionary politics, nationalism, class struggle, and anti-imperialism. For the first few months after the revolution, except for the National Front, the oldest liberal organization in Iran, and small Trotskyist group, Left and liberal parties remained ambivalent about women’s issues. They failed to recognize the remarkable contribution of women to the revolutionary struggle and the need to check the assault on their rights. At the time, most of the women’s organization operated as an appendix to different political parties to further the anti-imperialist struggle and tied women’s issues to greater demands for social justice.
The establishment of the Islamic Republic proved inconsistent with fundamental women’s formal and legal rights. Despite earlier assurances, on the eve of March 8, 1979, less than a month after the triumph of the revolution, Ayatollah Khomeini called upon the Provisional Government to uphold Islamic dress codes in its offices. His pronouncement scandalized many who played a significant role in the revolutionary movement, including several members of his own Revolutionary Council. This was the second time, after the abrogation of the Family Protection Law, in three weeks that issues of women’s right had become a point of contention in the postrevolutionary power struggle. That was why the festive preparations for the first postrevolutionary International Women’s Day turned into a rally with specific women’s rights demands such as the recognition of women judges and, most importantly, a call against compulsory hejāb. Thousands of women gathered in Tehran University and the next day in front of and inside the hallways of the Ministry of Justice chanting: In the Spring of freedom, absent is the rights of women.
Instituting compulsory hejāb even in the tightly controlled parliament and implementing it throughout the country was not an easy proposition. It took another four years for the mandate to become an enforceable law. Different factions inside the government as well as influential clerics in seminaries raised questions about the wisdom of such a law, its religious justification, as well as its feasibility. Nevertheless, the new law went into effect on August 9, 1983.
The institution of compulsory hejāb and other patriarchal measures in cases of travel, marriage, custody, inheritance, criminal laws, etc. all of which formally reduced women to second-class citizens, gave yet more credibility to feminist concerns that the Islamic republic would entirely force women out of the public sphere. Comparisons were made with Reza Shah. Some argued that whereas he liberated Muslim women by the “unveiling law” that banned the hejāb in public spaces in 1936, the Islamic Republic was now forcing women back into the private sphere where they would be subjected to the repressive domestic patriarchy. Yet curiously – these contrasting policies produced paradoxical results on the ground. Reza Shah’s “unveiling” did not liberate women, and the Islamic Republic’s repressive measures did not imprison women at home. Ironically, it was under Reza Shah’s “unveiling law” that a great majority of women in urban areas were forced to stay at home, either because they chose not to appear in public without a veil or were not allowed to leave their homes by their fathers or husbands. Under the Islamic Republic, despite the institution of repressive anti-women laws, rather than being imprisoned in their homes, women gained unprecedented mobility in the country and year after year increased their presence in the public sphere.
These were unintended consequences, but they were quite substantial. As a consequence of the restrictions imposed on women in public places, a new system emerged of what I call patriarchy by proxy. The new laws created the possibility for a great majority of socially conservative Iranian families who were previously reluctant to see women’s participation in social affairs, to trust the new “Islamized” public sphere as an extended domain of patriarchal/religious order. The state became the ultimate guardian of patriarchy and by becoming so, paradoxically, sanctioned an unprecedented mobility among rural and urban women. Despite barring women from entering key political and judicial positions of decision-making, women entered and shaped the conditions of those spheres in significant numbers.
(continued in right column)
Question related to this article:
Prospects for progress in women’s equality, what are the short and long term prospects?
(continued from left column)
In practice, gender politics and policy under the Islamic Republic have been far from the mere enactment of literal readings of the Qur’anic verses or a replication of women’s repression in Saudi Arabia. There is no doubt that the postrevolutionary regime instituted formal and legal apparatuses in order to constitute a homo Islamicus. But in its realpolitik, the Islamic Republic negated the anxieties that it would implement a literal reading of the Qur’an and expunge women from the pubic and restrict their lives to the domestic sphere. A quick look at the human development indexes in relation to women’s status in education, health, sports, artistic and cultural production, and civic engagement shows that the women in Iran have the most visible presence in public sphere in its history. These changes were not the result of top-down state policies, but rather the consequence of a contentious engagement between different factions within the polity, women’s community and civic institutions, and political parties and activists.
From the time of revolution in 1979 to the latest reports in 2019, women’s literacy rate rose from 36% to 97.93%; share of women students in higher education rose from 15% to 60%; women’s life expectancy rose from 55 to 77; infant mortality decreased from 90 per 1000 to 10 per 1000. None of these could have been possible without a remarkable presence of women in public space and their involvement in policy planning and implementation.
The significant presence of women in the public arena created unanticipated shifts in gender relations in the country, conditions that forced even the most patriarchal factions in power to advocate unlikely propositions regarding women’s role in society. In 2006-2007 school year, women comprised 60% of incoming class of university students, and that trend continues. The conservatives of the 8th Parliament introduced legislation for affirmative action for men to catch up with women in higher education. The conservative parliamentarians, who otherwise insist that the place of women is at home to raise a virtuous family, argued that women who use resources of free public universities had to commit to a 10-year employment (public or private) after graduation. The paradox there is self-evident.
Another measure that contributed to the remarkable shift in family structure and gendered relations in public and private spheres was an aggressive family planning and population control program that was instituted in 1989. Although the Islamic Republic repealed the family planning and protection laws of the old regime soon after assuming power, in a significant shift, in 1988, the government introduced and carried out one of the most efficient family planning programs in the economically developing world. Dictated by the perceived necessity of containing an unchecked rise in population, the program successfully reduced the population growth rate from the high of 3.4% in 1986 to 0.7% in 2007. During the same period, the number of children per family dropped from 6.5 to less than 2. Before his death in 1989, Ayatollah Khomeini endorsed the new program thus affording religious legitimacy to this ideological reversal. As the Candadian-Iranian anthropologists Homa Hoodfar has shown, without national consensus-building, a massive mobilization of women, both by government agencies as well as non-governmental agents, promoted with effective religious justification, and offered through an efficient delivery service in birth control and contraceptives (such as distribution of free condoms), and premarital sex-education programs, this ambitious family planning project could not have been realized. Called by many “The Iranian Miracle,” the program was so successful that, fearing the emergence of an aging population, the authorities are now trying to encourage families to have more children.
The purpose of this brisk history is not to draw a sanguine picture of women’s conditions in contemporary Iran. The complexities of how government and non-governmental actors interact on these issues, how the expansion and containment of state power shape the social realities of women of different classes and ethnicities, or how religious doctrines and convictions hinder or facilitate women’s mobility cannot be fully detailed here. Rather, I want to show that the Islamic Republic instituted policies and imposed patriarchal laws that produced unintended consequences in gender relations and women’s mobility. For an uprising to materialize, there needs to be a socially mobile, politically conscious, and subjectively free population. Iranian women have long been the fierce political actors we see on the street, not the oppressed, shadowy, veiled subjects that are the meat and potatoes of foreign misperception and paternalism. Yes, a mighty patriarchy shaped social order in Iran, like many other places in the world, but women were never its hapless captives. That image, the helpless veiled women, while effective in gathering support in global liberal feminist circles who believe that Muslim women need to be saved, does not correspond to the practice of those women’s everyday lives and fails to credit two generations of Iranian women for their political creativity.
At its core, Women-Life-Freedom is a movement for dignity and sovereignty of the subject. It is a movement that has changed the political culture of defiance and expressions of dissent. Its radical creativity— posters, songs, graffiti, and imaginative forms of collective action, has opened in practice the possibility of thinking of politics anew. The transformative acts of insubordinate bodies and liberated souls has made party platforms and unruffled sermons ineffective and obsolete.
While Iranian women and their male allies fight against the state’s brutal crackdown, their aspiring revolt, with its novel singularities, faces instrumentalization by regional and global actors, facilitated through a misreading of Iranian women’s history of deliberate and agentive action. While the global reach of this movement through the media operates as an instrument of its effective dissemination, paradoxically, it also subjects it to a discursive violence.
We should not misread the core principles of Women, Life, Freedom as being a simple “desire for the west” by a population who are simply fed up. Under such a misreading, a whole host of unsavory interests, from neocolonial expansionists to ethno-nationalist separatists, from delusional monarchists to all those who still lament being on the losing side of the 1979 revolution, try their best to claim ownership of this movement. Yet Iranian women on the ground have been the very actors who historically have created the conditions of possibility for their protest. They have opened space for themselves and their daughters in the face of a state desire for repressive patriarchy. Over decades they have succeeded to take advantage of the unintended consequences of state policies; they are not merely reacting—they are instead determined.
Today’s massive women’s movement in Iran represents one of the great achievements of the 1979 revolution—a revolution that generated hope-bearing, conscious subjects who have perpetuated themselves for more than four decades – despite and in the face of all manner of repression. The paradoxical effects of the Islamic Republic policies brought women to the centerstage of social transformation in Iran. Now that transformation has reached a point of frontal war with the state. Iranian women today hold key positions in journalism, artistic and cultural production, civic engagement, political organizing, higher education, scientific communities, local political offices, etc. Daughters of those women, irrevocably demand an extension and expansion of their mothers’ positions without any patriarchal restrictions, either by the state or inside their homes.
Those demands will only be realized through the transformation of the state, or by rethinking the meaning of the state. How this transformation will unfold and with what means is yet not known, but its inevitability is evident. How fortunate we are that these generations of women taking the lead.
– – – – –
Behrooz Ghamari-Tabrizi is an Iranian-born American historian, sociologist, and professor.

 video about the new bases tool
video about the new bases tool









