DISARMAMENT & SECURITY .
An article by Daryl G. Kimball and Shizuka Kuramitsu in Global Issues
Japanese Foreign Minister Yoko Kamikawa a rare, high-level UN Security Council meeting on nuclear disarmament and nonproliferation on March 18.
Although the meeting underscored the urgency of addressing the growing threats posed by nuclear weapons, it also highlighted the chronic divisions among key states on disarmament and nonproliferation issues.
“The world now stands on the cusp of reversing decades of declines in nuclear stockpiles. We will not stop moving ahead to promote realistic and practical efforts to create a world without nuclear weapons. Japan cannot accept Russia’s threats to break the world’s 78-year record of the nonuse of nuclear weapons,” she added.
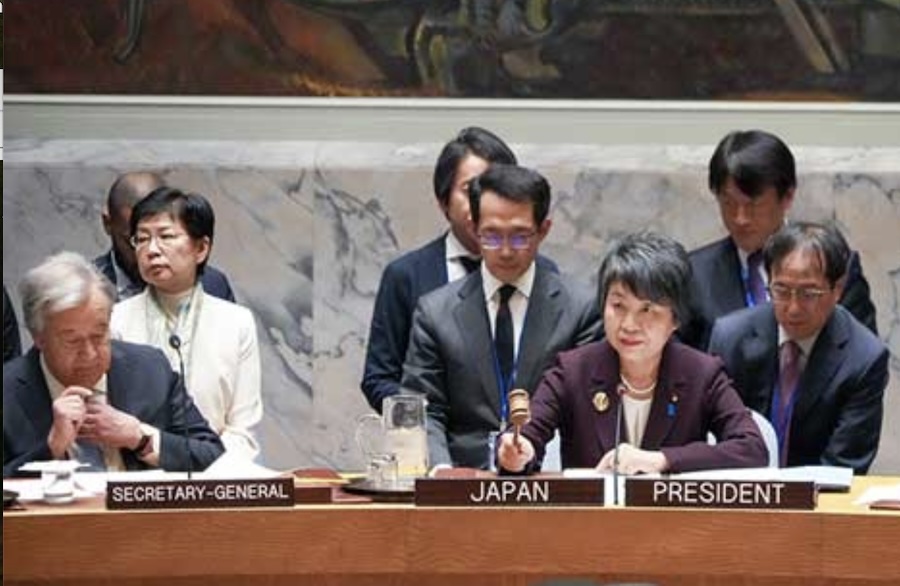

Japanese Foreign Minister Yoko Kamikawa chairs a UN Security Council meeting on nuclear disarmament in New York on March 18. She has warned that “the world now stands on the cusp of reversing decades of declines in nuclear stockpiles.” Credit: Japanese Foreign Ministry
UN Secretary-General António Guterres; Robert Floyd, executive secretary of the Preparatory Commission of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization; and Gaukhar Mukhatzhanova, director of the nonproliferation program at the Vienna Center for Disarmament and Non-Proliferation, were invited to brief the meeting.
All Security Council members were represented, including the five permanent members (China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States). Many stressed the urgency of addressing growing nuclear weapons threats.
But the exchange also underscored the extent to which rising geopolitical tensions and long-standing divisions among leading states impede tangible progress on disarmament and nonproliferation issues.
In his opening remarks, Guterres warned that “umanity cannot survive a sequel to Oppenheimer. Voice after voice, alarm after alarm, survivor after survivor are calling the world back from the brink.”
“And what is the response?” he asked. “States possessing nuclear weapons are absent from the table of dialogue. Investments in the tools of war are outstripping investments in the tools of peace. Arms budgets are growing, while diplomacy and development budgets are shrinking.”
Guterres said the nuclear-armed states in particular “must re-engage” to prevent any use of a nuclear weapon, including by securing a no-first-use agreement, stopping nuclear saber-rattling, and reaffirming moratoriums on nuclear testing.
He urged them to take action on prior disarmament commitments under the nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty (NPT), including reductions in the number of nuclear weapons “led by the holders of the largest nuclear arsenals, the United States and the Russian Federation, who must find a way back to the negotiating table to fully implement the and agree on its successor.”
To catalyze action, he reiterated his call for “reforms to disarmament bodies, including the Conference on Disarmament …that could lead to a long-overdue fourth special session of the General Assembly devoted to disarmament.”
U.S. Ambassador Linda Thomas-Greenfield criticized Russia’s “irresponsible…nuclear rhetoric” and said that “China has rapidly and opaquely built up and diversified” its nuclear arsenal. In addition, “Russia and China have remained unwilling to engage in substantive discussions around arms control and risk reduction,” she said.
Thomas-Greenfield reiterated the U.S. offer to “engage in bilateral arms control discussions with Russia and China, right now, without preconditions.”
Dmitry Polyanskiy, Russia’s deputy UN ambassador, said that his country shares “the noble goal” of a nuclear-weapon-free world. Nevertheless, he described the possession of nuclear weapons as “an important factor in maintaining the strategic balance.”
(Continued in right column)
Can we abolish all nuclear weapons?
(Continued from left column)
Polyanskiy countered criticism of Russian nuclear threats by charging that it is the “clearly Russo-phobic line of the United States and its allies creates risks of escalation that threaten to trigger a direct military confrontation among nuclear powers.”
He said the current situation is largely the result of the “years-long policy of the United States and its allies aimed at undermining the international architecture of arms control, disarmament, and nonproliferation.”
Polyanskiy added, “As for the issues of strategic dialogue between Russia and the United States with a view to new agreements on nuclear arms control, they cannot be isolated from the general military-political context. We see no basis for such work in the context of Western countries’ attempts to inflict a ‘strategic defeat’ on Russia and their refusal to respect our vital interests.”
Maltese Ambassador Vanessa Frazier called on the nuclear-weapon states to fulfill their disarmament obligations under the NPT. “Current tensions cannot be an excuse for the delay…. Rather they should be a reason to accelerate the implementation,” she said.
Chinese Ambassador Zhang Jun acknowledged that “the risk of a nuclear arms race and a nuclear conflict is rising” and “he road to nuclear disarmament remains long and arduous.”
He reiterated Beijing’s long-standing position that “nuclear weapons states should explore feasible measures to reduce strategic risks, negotiate and conclude a treaty on no first use of nuclear weapons against each other” and “provide legally binding negative security assurances to non-nuclear-weapon states.”
Apparently in response to U.S. criticism of a Chinese nuclear buildup and refusal to engage in substantive arms control and risk reduction talks, Zhang said these “allegations against China do not hold any water.”
“Demanding that countries with vastly different nuclear policies and number of nuclear weapons should assume the same level of nuclear disarmament and nuclear transparency obligations is not consistent with the logic of history and reality, nor is it in line with international consensus, and as such will only lead international nuclear disarmament to a dead end,” the Chinese envoy said.
Some states proposed new initiatives. In response to U.S. concerns that Russia may be pursuing an orbiting anti-satellite system involving a nuclear explosive device, Japan and the United States announced they will “put forward a Security Council resolution, reaffirming the fundamental obligations that parties have under this Treaty,” which prohibits the deployment of weapons in space. (See ACT, March 2024.)
Japan also announced the establishment of a cross-regional group called Friends of FMCT “with the aim to maintain and enhance political attention” and to expand support for negotiating a fissile material cutoff treaty (FMCT) banning the production of fissile materials for nuclear weapons.
For decades, the 65-nation CD has failed to agree on a path to begin FMCT talks. Australia, Brazil, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Nigeria, the Philippines, the UK, and the United States will join the FMCT group, according to the Japanese Foreign Ministry.
High-level Security Council debates focused on nuclear disarmament and nonproliferation have been infrequent in the post-Cold War era, and few of them result in consensus statements or resolutions.
In 2009, the council held a summit-level meeting chaired by U.S. President Barack Obama on nuclear nonproliferation and disarmament. It adopted Resolution 1887, which reaffirmed a “commitment to the goal of a world free of nuclear weapons” and outlined a framework of measures for reducing global nuclear dangers.
In September 2016, the council adopted Resolution 2310, which reaffirmed support for the 1996 Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty. It called on states to refrain from resuming nuclear testing and called on states that have not signed or ratified the treaty to do so without further delay.
More recently, the council has held briefings on nuclear disarmament issues but without tangible outcomes.
The last such meetings were in March 2023, when Mozambique chaired a discussion on threats to international peace and security, including nuclear dangers, and in August 2022, when China organized a meeting on promoting common security through dialogue in the context of escalating tensions among major nuclear powers.
– – – – – –
If you wish to make a comment on this article, you may write to coordinator@cpnn-world.org with the title “Comment on (name of article)” and we will put your comment on line. Because of the flood of spam, we have discontinued the direct application of comments.