FREE FLOW OF INFORMATION
An article by Eric Zuesse in Transcend Media Service
8 Feb 2019 – This news-report is being submitted to all U.S. and allied news-media, and is being published by all honest ones, in order to inform you of crucial facts that the others — the dishonest ones, that hide such crucial facts — are hiding about Venezuela. These are facts that have received coverage only in one single British newspaper: the Independent, which published a summary account of them on January 26th. That newspaper’s account will be excerpted here at the end, but first will be highlights from its topic, the official report to the U.N. General Assembly in August of last year, which has been covered-up ever since. This is why that report’s author has now gone to the Independent, desperate to get the story out, finally, to the public.
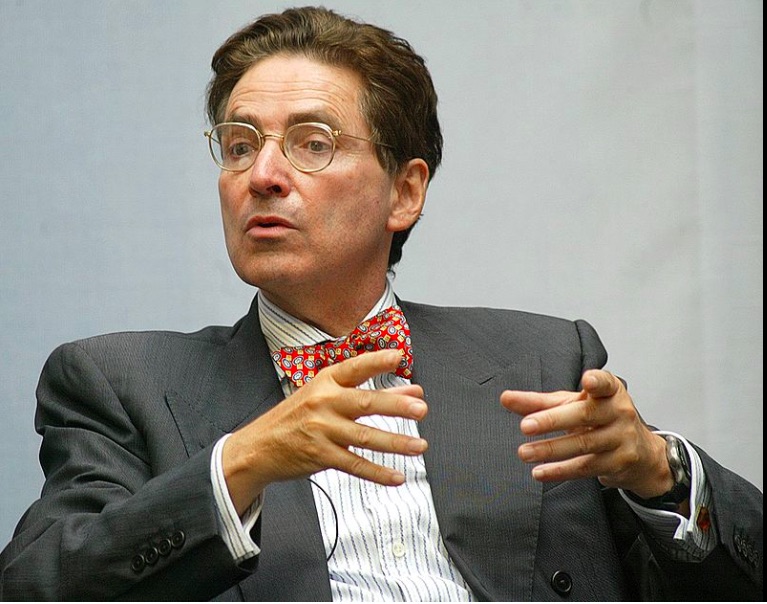

Alfred de Zayas, UN Independent Expert on the Promotion of a Democratic and Equitable International Order (appointed by the United Nations Human Rights Council)
The Covered-Up Document
On 3 August 2018, the U.N.’s General Assembly received the report from the U.N.s Independent Expert on the Promotion of a Democratic and Equitable International Order, concerning his mission to Venezuela and Ecuador. His recent travel though both countries focused on “how best to enhance the enjoyment of all human rights by the populations of both countries.” He “noted the eradication of illiteracy, free education from primary school to university, and programmes to reduce extreme poverty, provide housing to the homeless and vulnerable, phase out privilege and discrimination, and extend medical care to everyone.” He noted “that the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, and Ecuador, both devote around 70 per cent of their national budgets to social services.” However (and here, key paragraphs from the report are now quoted):
*****
22. Observers have identified errors committed by the Chávez and Maduro Governments, noting that there are too many ideologues and too few technocrats in public administration, resulting in government policies that lack coherence and professional management and discourage domestic investment, already crippled by inefficiency and corruption, which extend to government officials, transnational corporations and entrepreneurs. Critics warn about the undue influence of the military on government and on the running of enterprises like Petróleos de Venezuela. The lack of regular, publicly available data on nutrition, epidemiology and inflation are said to complicate efforts to provide humanitarian support.
23. Meanwhile, the Attorney General, Tarek Saab, has launched a vigorous anticorruption campaign, investigating the links between Venezuelan enterprises and tax havens, contracting scams, and deals by public officials with Odebrecht. It is estimated that corruption in the oil industry has cost the Government US$ 4.8 billion. The Attorney General’s Office informed the Independent Expert of pending investigations for embezzlement and extortion against 79 officials of Petróleos de Venezuela, including 22 senior managers. The Office also pointed to the arrest of two high-level oil executives, accused of money-laundering in Andorra. The Ministry of Justice estimates corruption losses at some US$ 15 billion. Other stakeholders, in contrast, assert that anti-corruption programmes are selective and have not sufficiently targeted State institutions, including the military. …
29. … Over the past sixty years, non-conventional economic wars have been waged against Cuba, Chile, Nicaragua, the Syrian Arab Republic and the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela in order to make their economies fail, facilitate regime change and impose a neo-liberal socioeconomic model. In order to discredit selected governments, failures in the field of human rights are maximized so as to make violent overthrow more palatable. Human rights are being “weaponized” against rivals. Yet, human rights are the heritage of every human being and should never be instrumentalized as weapons of demonization. …
30. The principles of non-intervention and non-interference in the internal affairs of sovereign States belong to customary international law and have been reaffirmed in General Assembly resolutions, notably [a list is supplied]. …
31. In its judgment of 27 June 1986 concerning Nicaragua v. United States, the International Court of Justice quoted from [U.N.] resolution 2625 (XXV): “no State shall organize, assist, foment, finance, incite or tolerate subversive, terrorist or armed activities directed towards the violent overthrow of the regime of another State, or interfere in civil strife in another State”. …
36. The effects of sanctions imposed by Presidents Obama and Trump and unilateral measures by Canada and the European Union have directly and indirectly aggravated the shortages in medicines such as insulin and anti-retroviral drugs. To the extent that economic sanctions have caused delays in distribution and thus contributed to many deaths, sanctions contravene the human rights obligations of the countries imposing them.Moreover, sanctions can amount to crimes against humanity under Article 7 of the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court. An investigation by that Court would be appropriate, but the geopolitical submissiveness of the Court may prevent this.
37. Modern-day economic sanctions and blockades are comparable with medieval sieges of towns with the intention of forcing them to surrender. Twenty-first century sanctions attempt to bring not just a town, but sovereign countries to their knees. A difference, perhaps, is that twenty-first century sanctions are accompanied by the manipulation of public opinion through “fake news”, aggressive public relations and a pseudo-human rights rhetoric so as to give the impression that a human rights “end” justifies the criminal means. …
39. Economic asphyxiation policies are comparable to those already practised in Chile, the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, Nicaragua and the Syrian Arab Republic. In January 2018, Middle East correspondent of The Financial Times and The Independent, Patrick Cockburn, wrote on the sanctions affecting Syria: There is usually a pretence that foodstuffs and medical equipment are being allowed through freely and no mention is made of the financial and other regulatory obstacles making it impossible to deliver them. An example of this is the draconian sanctions imposed on Syria by the US and EU which were meant to target President Bashar al-Assad and help remove him from power. They have wholly failed to do this, but a UN internal report leaked in 2016 shows all too convincingly the effect of the embargo in stopping the delivery of aid by international aid agencies. They cannot import the aid despite waivers because banks and commercial companies dare not risk being penalised for having anything to do with Syria. The report quotes a European doctor working in Syria as saying that “the indirect effect of sanctions … makes the import of the medical instruments and other medical supplies immensely difficult, near impossible”. In short: economic sanctions kill. …
41. Bearing in mind that Venezuelan society is polarized, what is most needed is dialogue between the Government and the opposition, and it would be a noble task on the part of the Secretary-General of the United Nations to offer his good offices for such a dialogue. Yet, opposition leaders Antonio Ledezma and Julio Borges, during a trip through Europe to denounce the Government of the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, called for further sanctions as well as a military “humanitarian intervention”. …
44. Although the situation in the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela has not yet reached the humanitarian crisis threshold, there is hunger, malnutrition, anxiety, anguish and emigration. What is crucial is to study the causes of the crisis, including neglected factors of sanctions, sabotage, hoarding, black market activities, induced inflation and contraband in food and medicines.
45. The “crisis” in the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela is an economic crisis, which cannot be compared with the humanitarian crises in Gaza, Yemen, Libya, the Syrian Arab Republic, Iraq, Haiti, Mali, the Central African Republic, South Sudan, Somalia, or Myanmar, among others. It is significant that when, in 2017, the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela requested medical aid from the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, the plea was rejected, because it ”is still a high-income country … and as such is not eligible”. …
(Article continued in the right column.)
Free flow of information, How is it important for a culture of peace?
What is really happening in Venezuela?
Are economic sanctions a violation of human rights?
(Article continued from left column)
46. It is pertinent to recall the situation in the years prior to the election of Hugo Chávez. Corruption was ubiquitous and in 1993, President Carlos Pérez was removed because of embezzlement. The Chávez election in 1998 reflected despair with the corruption and neo-liberal policies of the 1980s and 1990s, and rejection of the gulf between the super-rich and the abject poor.
47. Participatory democracy in the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, called “protagónica”, is anchored in the Constitution of 1999 and relies on frequent elections and referendums. During the mission, the Independent Expert exchanged views with the Electoral Commission and learned that in the 19 years since Chávez, 25 elections and referendums had been conducted, 4 of them observed by the Carter Center. The Independent Expert met with the representative of the Carter Center in the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, who recalled Carter’s positive assessment of the electoral system. They also discussed the constitutional objections raised by the opposition to the referendum held on 30 July 2017, resulting in the creation of a Constitutional Assembly. Over 8 million Venezuelans voted in the referendum, which was accompanied by international observers, including from the Council of Electoral Specialists of Latin America.
48. An atmosphere of intimidation accompanied the mission, attempting to pressure the Independent Expert into a predetermined matrix. He received letters from NGOs asking him not to proceed because he was not the “relevant” rapporteur, and almost dictating what should be in the report. Weeks before his arrival, some called the mission a “fake investigation”. Social media insults bordered on “hate speech” and “incitement”. Mobbing before, during and after the mission bore a resemblance to the experience of two American journalists who visited the country in July 2017. Utilizing platforms such as Facebook and Twitter, critics questioned the Independent Expert’s integrity and accused him of bias, demonstrating a culture of intransigence and refusal to accept the duty of an independent expert to be neutral, objective, dispassionate and to apply his expertise free of external pressures. …
67. The Independent Expert recommends that the General Assembly: (g) Invoke article 96 of the Charter of the United Nations and refer the following questions to the International Court of Justice: Can unilateral coercive measures be compatible with international law? Can unilateral coercive measures amount to crimes against humanity when a large number of persons perish because of scarcity of food and medicines? What reparations are due to the victims of sanctions? Do sanctions and currency manipulations constitute geopolitical crimes? (h) Adopt a resolution along the lines of the resolutions on the United States embargo against Cuba, declaring the sanctions against the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela contrary to international law and human rights law. …
70. The Independent Expert recommends that the International Criminal Court investigate the problem of unilateral coercive measures that cause death from malnutrition, lack of medicines and medical equipment. …
72. The Independent Expert recommends that, until the International Court of Justice and the International Criminal Court address the lethal outcomes of economic wars and sanctions regimes, the Permanent Peoples Tribunal, the Russell Tribunal and the Kuala Lumpur War Crimes Commission undertake the task so as to facilitate future judicial pronouncements.
****
On January 26th, Britain’s Independent headlined “Venezuela crisis: Former UN rapporteur says US sanctions are killing citizens”, and Michael Selby-Green reported that:
The first UN rapporteur to visit Venezuela for 21 years has told The Independent the US sanctions on the country are illegal and could amount to “crimes against humanity” under international law.
Former special rapporteur Alfred de Zayas, who finished his term at the UN in March, has criticized the US for engaging in “economic warfare” against Venezuela which he said is hurting the economy and killing Venezuelans.
The comments come amid worsening tensions in the country after the US and UK have backed Juan Guaidó, who appointed himself “interim president” of Venezuela as hundreds of thousands marched to support him. …
The US Treasury has not responded to a request for comment on Mr de Zayas’s allegations of the effects of the sanctions programme.
US sanctions prohibit dealing in currencies issued by the Venezuelan government. They also target individuals, and stop US-based companies or people from buying and selling new debt issued by PDVSA or the government.
The US has previously defended its sanctions on Venezuela, with a senior US official saying in 2018: “The fact is that the greatest sanction on Venezuelan oil and oil production is called Nicolas Maduro, and PDVSA’s inefficiencies,” referring to the state-run oil body, Petroleos de Venezuela, SA.
Mr De Zayas’s findings are based on his late-2017 mission to the country and interviews with 12 Venezuelan government ministers, opposition politicians, 35 NGOs working in the country, academics, church officials, activists, chambers of commerce and regional UN agencies.
The US imposed new sanctions against Venezuela on 9 March 2015, when President Barack Obama issued executive order 13692, declaring the country a threat to national security.
The sanctions have since intensified under Donald Trump, who has also threatened military invasion and discussed a coup. …
Despite being the first UN official to visit and report from Venezuela in 21 years, Mr de Zayas said his research into the causes of the country’s economic crisis has so far largely been ignored by the UN and the media, and caused little debate within the Human Rights Council.
He believes his report has been ignored because it goes against the popular narrative that Venezuela needs regime change. …
The then UN high commissioner, Zeid Raad Al Hussein, reportedly refused to meet Mr de Zayas after the visit, and the Venezuela desk of the UN Human Rights Council also declined to help with his work after his return despite being obliged to do so, Mr de Zayas claimed. …
Ivan Briscoe, Latin America and Caribbean programme director for Crisis Group, an international NGO, told The Independent that Venezuela is a polarising subject. … Briscoe is critical of Mr de Zayas’ report because it highlights US economic warfare but in his view neglects to mention the impact of a difficult business environment in the country. … Briscoe acknowledged rising tensions and the likely presence of US personnel operating covertly in the country. …
Eugenia Russian, president of FUNDALATIN, one of the oldest human rights NGOs in Venezuela, founded in 1978 before the Chavez and Maduro governments and with special consultative status at the UN, spoke to The Independent on the significance of the sanctions.
“In contact with the popular communities, we consider that one of the fundamental causes of the economic crisis in the country is the effect that the unilateral coercive sanctions that are applied in the economy, especially by the government of the United States,” Ms Russian said.
She said there may also be causes from internal errors, but said probably few countries in the world have suffered an “economic siege” like the one Venezuelans are living under. …
In his report, Mr de Zayas expressed concern that those calling the situation a “humanitarian crisis” are trying to justify regime change and that human rights are being “weaponised” to discredit the government and make violent overthrow more “palatable”….
Venezuela has the largest oil reserves in the world and an abundance of other natural resources including gold, bauxite and coltan. But under the Maduro government they’re not easily accessible to US and transnational corporations.
US oil companies had large investments in Venezuela in the early 20th century but were locked out after Venezuelans voted to nationalise the industry in 1973.
Other than readers of that single newspaper, where has the public been able to find these facts? If the public can have these facts hidden from them, then how much trust should the public reasonably have in the government, and in the news-media?