. . SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT . .
An article from Xinhua, China News (with links added by CPNN)
Leaders of developing countries gathered in the Ugandan capital of Kampala over the past week, reaching a consensus to promote South-South cooperation to enhance their capability of pursuing sustainable development, seek strength from unity and increase the role of the Global South in international affairs.
High-level representatives of more than 100 countries and heads of United Nations agencies attended the 19th Summit of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) that concluded on Saturday and the 3rd South Summit of the Group of 77 (G77) that wrapped up on Monday.
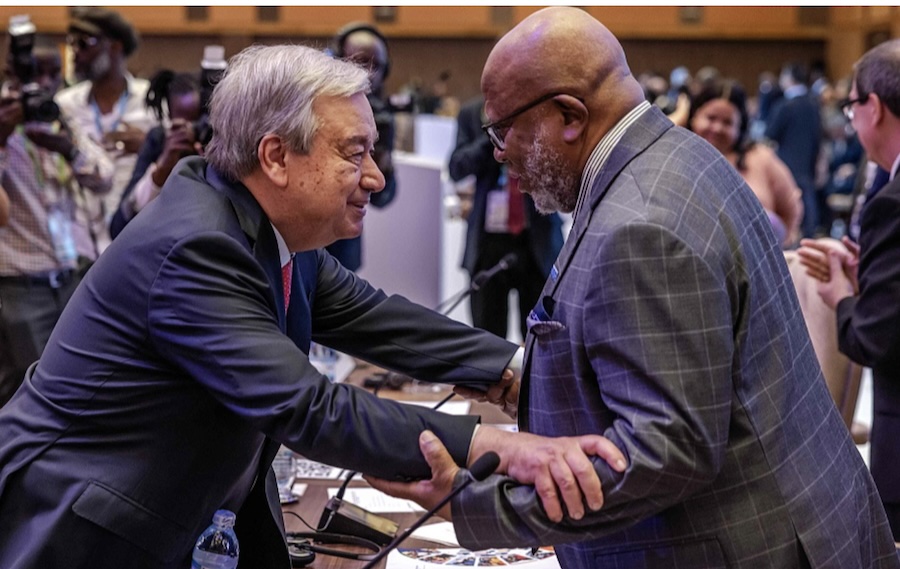

UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres (L) greets President of the UN General Assembly Dennis Francis (R) during the opening session of the Third South Summit of the Group of 77 and China in Kampala, January 21, 2024. /CFP
Participants said they are optimistic about the future of the Global South in world affairs, gearing up to influence the outcomes of the UN Summit of the Future scheduled for September in New York. UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres described the September summit as a once-in-a-generation opportunity to reinvigorate global action, recommit to fundamental principles, and further develop the frameworks of multilateralism so they are fit for the future.
In the outcome documents of the two summits, the countries of the Global South said they hope to play an influential role in shifting the balance of the geopolitical landscape from conflict, confrontation and mistrust to diplomacy, dialogue, peace and understanding.
NAM countries, in their declaration over the weekend, said they would positively contribute to the summit to enhance cooperation on critical challenges and address gaps in global governance.
Developing nations stressed that there is a need to reform the multilateral global governance architecture, including the United Nations and the international financial system. This reform would make the institutions fit for purpose, democratic, equitable, representative and responsive to the current global realities and the needs and aspirations of the Global South, according to the NAM Kampala Declaration.
(Article continued in the column on the right)
(Click here for the original Spanish version of the article)
How can ensure that development is equitable?
Where in the world can we find good leadership today?
(Article continued from the column on the left)
They said the current violation of international laws and UN resolutions on the Israeli-Palestinian crisis, coupled with the unfair treatment of developing countries facing debt distress amid a slow-growing global economy, are the key issues that have revitalized the call for a reformed global system.
Ugandan President Yoweri Museveni, who is also the chairperson of the NAM Summit, said the forum should be used to exercise considerable influence, particularly at the UN, for an effective transformative process. “In the negotiations for the Pact of the Future, the outcome document of the upcoming UN Summit of the Future, we should clearly define priorities that favor developing countries by maintaining unity, solidarity, and collective coordination among member states,” Museveni said.
Dennis Francis, president of the UN General Assembly, said addressing the current global challenges requires creativity and consensus-building to fashion effective solutions.
Francis said the current crises, ranging from the Ukraine-Russia, Israel-Palestine and those in Africa, raise questions about the relevance and value of the UN in terms of its ability to resolve global issues. He argued that the Summit of the Future will offer a historic opportunity to forge a new global consensus to transform the multilateral system to deliver better impact for people.
The Global South, according to Secretary-General Guterres, bears the responsibility of changing the form of the global system, noting that those who currently benefit from it are unlikely to lead its reform.
“We have a chance to cultivate a just, peaceful, and prosperous future, where no one is left behind. But for that, a lot needs to be changed and reformed. Together, let’s unite and fight to make that a reality,” Guterres told the 3rd South Summit on Sunday.
He urged the international community to reform and revitalize multilateralism so that it works for everyone, everywhere, and meets the challenges of today. “We rely on the G77 plus China to make the Summit of the Future a success. To seize this opportunity and to find common solutions. The summit will consider deep reforms of the international financial architecture,” the UN top envoy said.
(Editor’s note. Putting the terms “Group of 77” and “Kampala” into the Google search engine for the preceding month on February 16, we found articles about the event above from press in Uganda, India, Brazil, Bahamas, Philippines, South Africa, Jordan, Angola, Turkey, Sri Lanka, Guyana, Pakistan, Saint Vincent, Bhutan, Namibia, Cameroon, Yemen, Mongolia, Tanzania, Myanmar, Morocco, Cuba, Maldives, Kenya, Eritrea, Mozambique, Nigeria, Malaysia, Oman, Seychelles, Zimbabwe and Somalia, as well as from China and from the United Nations, but with the exception of an agency by the name of Newsbeezer, ABSOLOUTELY NO ARTICLE IN ENGLISH from a press agency based in Europe or North America! By using other languages, we found an article in French in the news site of l’Humanité which remarked that the event was totally ignored by the West (” un événement totalement passé sous silence dans les pays occidentaux”>. And in Spain, one could read about the event in Spanish on the news media that subscribe to EFE. )