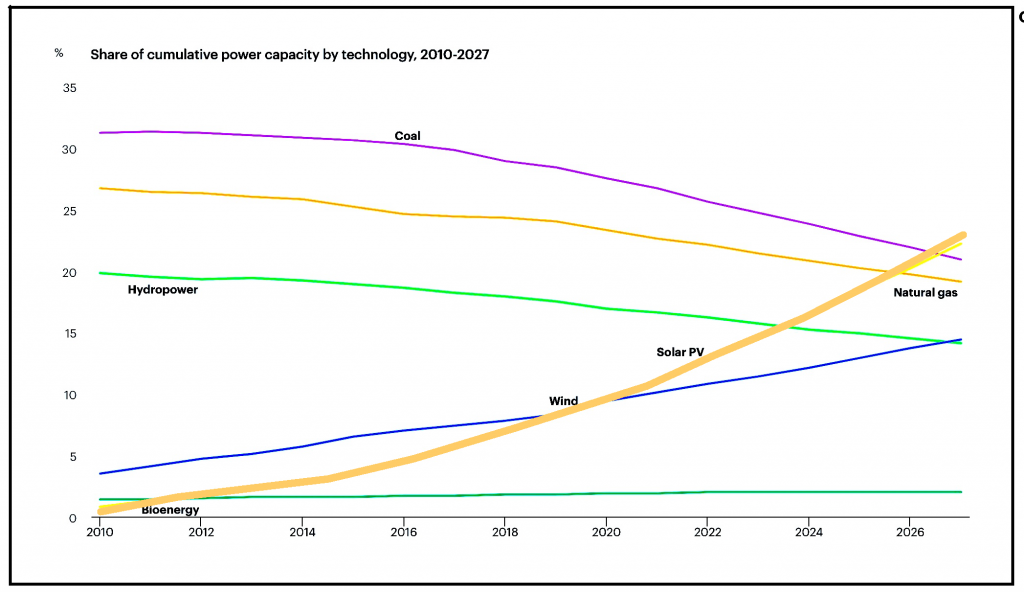
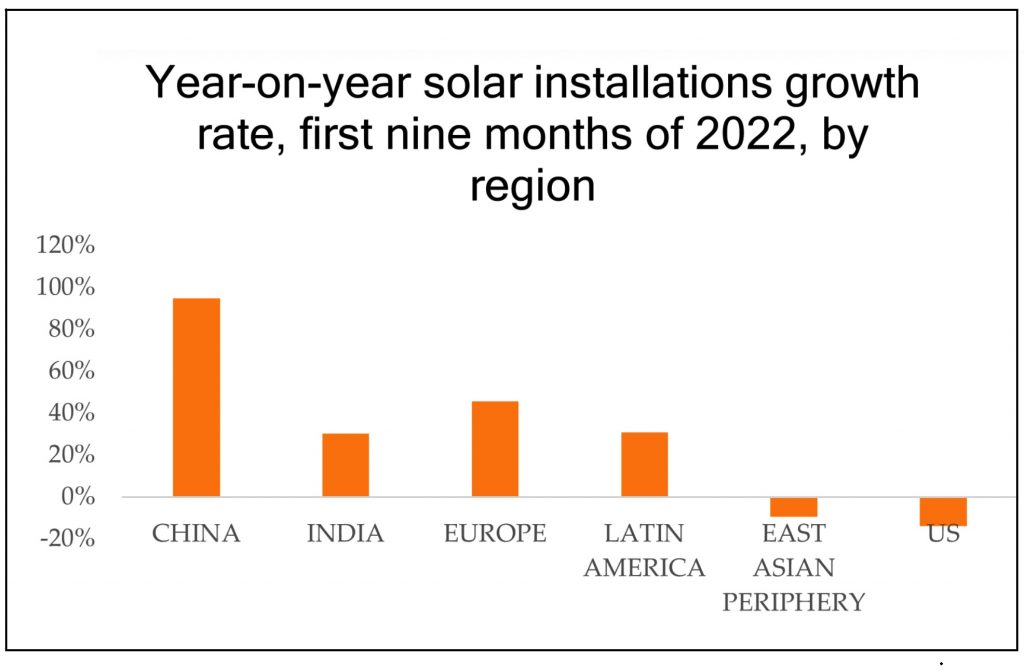
. . SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT . .
An article by Kenny Stancil in Common Dreams
Delegates to the Havana Congress on the New International Economic Order—a gathering organized by the Progressive International and attended by more than 50 scholars and policymakers from 26 countries across all six inhabited continents—agreed over the weekend on a declaration that outlines a “common vision” for building an egalitarian and sustainable society out of the wreckage of five decades of neoliberal capitalism.
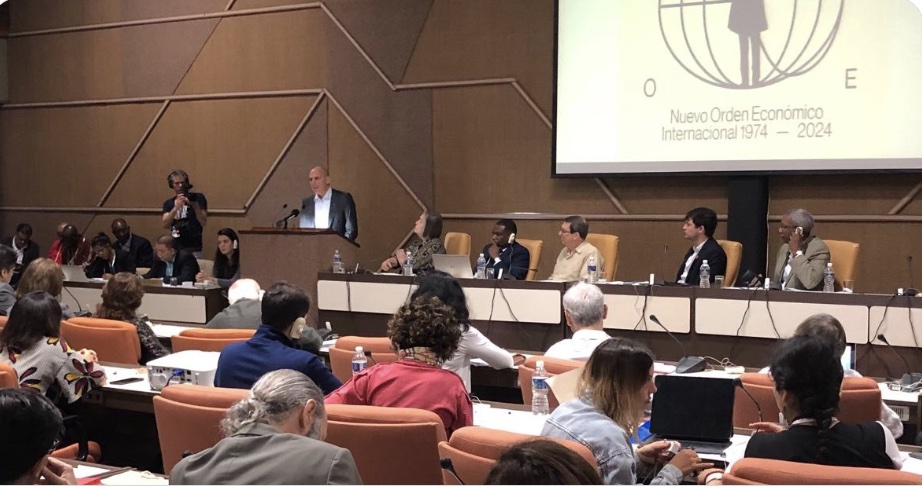

(Click on photo to enlarge)
“The crisis of the existing world system can either entrench inequalities,” the declaration asserts, or it can “embolden” popular movements throughout the Global South to “reclaim” their role as protagonists “in the construction of a new world order based on justice, equity, and peace.”
Delegates resolved to focus their initial efforts on strengthening the development and dissemination of lifesaving technologies in low-income nations.
This decision comes one year after Cuban officials announced, at a press conference convened by the Progressive International (PI), their plan to deliver 200 million homegrown Covid-19 vaccine doses to impoverished countries abandoned by their wealthy counterparts and Big Pharma—along with tools to enable domestic production and expert support to improve distribution.
It also comes as Cuba assumes the presidency of the Group of 77 (G77), a bloc of 134 developing countries in Africa, Asia, and Latin America where “the combined crises of food, energy, and environment” are escalating, PI noted.
“What is the common vision to guide the Global South out of this crisis?” the coalition asked. “What is the plan to win it? What is the New International Economic Order for the 21st century?”
“After two days of detailed discussions about how to transform our shared world, delegates agreed that a key priority must be to secure science and technology sovereignty,” PI general coordinator David Adler said Sunday at the conclusion of the Havana Congress. “From pharmaceuticals to green tech, from digital currencies to microchips, too much of humanity is locked out of both benefiting from scientific advances and contributing to new ones. We will, as today’s declaration calls for, work to build ‘a planetary bloc led by the South and reinforced by the solidarities of the North’ to liberate knowledge and peoples.”
Speaking at the January 12 ceremony during which Cuba ascended to the G77 presidency, Cuban Foreign Minister Bruno Rodríguez Parrilla emphasized the need for coordinated action across the Global South on science and tech, arguing that “scientific-technical development is today monopolized by a club of countries that monopolize most of the patents, technologies, research centers, and promote the drain of talent from our countries.”
The G77 Summit on Science, Technology, and Innovation, scheduled for September in Havana, seeks to “unite, complement each other, integrate our national capacities so as not to be relegated to future pandemics,” said Parrilla.
During his speech on the first day of the Havana Congress, meanwhile, former Greek Finance Minister Yanis Varoufakis called for a new non-aligned movement to “end the legalized robbery of people and Earth fueling climate catastrophe.”
(Article continued in the column on the right)
(Click here for the original Spanish version of the article)
How can ensure that development is equitable?
Where in the world can we find good leadership today?
(Article continued from the column on the left)
Read the full Havana Declaration on the New International Economic Order:
The Havana Congress,
Recalling the role of the Cuban Revolution in the struggle to unite the Southern nations of the world, and the spirit of the 1966 Havana Tricontinental Conference that convened peoples from Asia, Africa, and Latin America to chart a path to collective liberation in the face of severe global crises and sustained imperial subjugation;
Hearing the echoes of that history today, as crises of hunger, disease, and war once again overwhelm the world, compounded by a rapidly changing climate and the droughts, floods, and hurricanes that not only threaten to inflame conflicts between peoples, but also risk the extinction of humanity at large;
Celebrating the legacy of the anti-colonial struggle, and the victories won by combining a program of sovereign development at home, solidarity for national liberation abroad, and a strong Southern bloc to force concessions to its interests, culminating in the adoption of the U.N. Declaration on the Establishment of a New International Economic Order (NIEO);
Acknowledging that the project of decolonization remains incomplete, disrupted by concerted attacks on the unity of the South in the form of wars, coups, sanctions, structural adjustment, and the false promise that sovereign development might be won through integration into a hierarchical world system;
Emphasizing that the result has been the sustained divergence between North and South, characterized by the same dynamics that defined the international economic order five decades prior: the extraction of natural resources, the enclosure of ‘intellectual property,’ the plunder of structural adjustment, and the exclusion of the multilateral system;
Recognizing that despite these setbacks, the flame of Southern resistance did not die; that the pursuit of sovereign development has yielded unprecedented achievements—from mass literacy and universal healthcare to poverty alleviation and medical innovation—that enable a renewed campaign of Southern cooperation today;
Stressing that this potential for Southern unity is perceived as a threat to Northern powers, which seek once again to preserve their position in the hierarchy of the world system through mechanisms of economic exclusion, political coercion, and military aggression;
Seizing the opportunity of the present historical juncture, when the crisis of the existing world system can either entrench inequalities or embolden the call to reclaim Southern protagonism in the construction of a new world order based on justice, equity, and peace;
The Havana Congress calls to:
* Renew the Non-Aligned Movement: In the face of increasing geopolitical tensions born from a decisive shift in the global balance of power, the Congress calls to resist the siren song of the new Cold War and to renew the project of non-alignment, grounded in the principles of sovereignty, peace, and cooperation articulated at the 1955 Bandung Conference, 1961 Non-Aligned Conference, 1966 Tricontinental Conference, and beyond.
* Renovate the NIEO: To accompany the renewed non-aligned movement, the Congress calls to renovate the vision for a New International Economic Order fit for the 21st century; a vision that must draw inspiration from the original Declaration, but also account for the key issues—from digital technology to environmental breakdown—that define the present conditions for sovereign development; and to enshrine this vision in a new U.N. Declaration on the occasion of its 50th anniversary.
* Assert Southern Power: The Congress recognizes that economic liberation will not be granted, but must be seized. As the original call for a New International Economic Order was won through the exercise of collective power in the coordinated production of petroleum, so our vision today can only be realized through the collective action of the South and the formation of new and alternative institutions to share critical technology, tackle sovereign debt, drive development finance, face future pandemics together, as well as coordinate positions on international climate action and the protection of national sovereignty over the extraction of natural resources.
* Accompany Cuba in the G77: The Congress recognizes the critical opportunity afforded by Cuba’s presidency of the Group of 77 plus China to lead the South out of the present crisis and channel the lessons of its Revolution toward concrete proposals and ambitious initiatives to transform the broader international system.
* Build a Planetary Bloc: The Congress calls on all peoples and nations of the world to join in this struggle to definitively achieve the New International Economic Order; to build a planetary bloc led by the South and reinforced by the solidarities of the North, whose peoples recognize their obligation to resist the crimes committed in their names; and to bring the spirit of this Havana Congress into the communities that we call home.