. . SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT . .
An article from Reuters (reprinted by permission)
Eight Amazon nations agreed to a list of unified environmental policies and measures to bolster regional cooperation at a major rainforest summit in Brazil on Tuesday (August 8), but failed to agree on a common goal for ending deforestation.
Brazilian President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva, who has staked his international reputation on improving Brazil’s environmental standing, had been pushing for the region to unite behind a common policy of ending deforestation by 2030 – one he has already adopted.
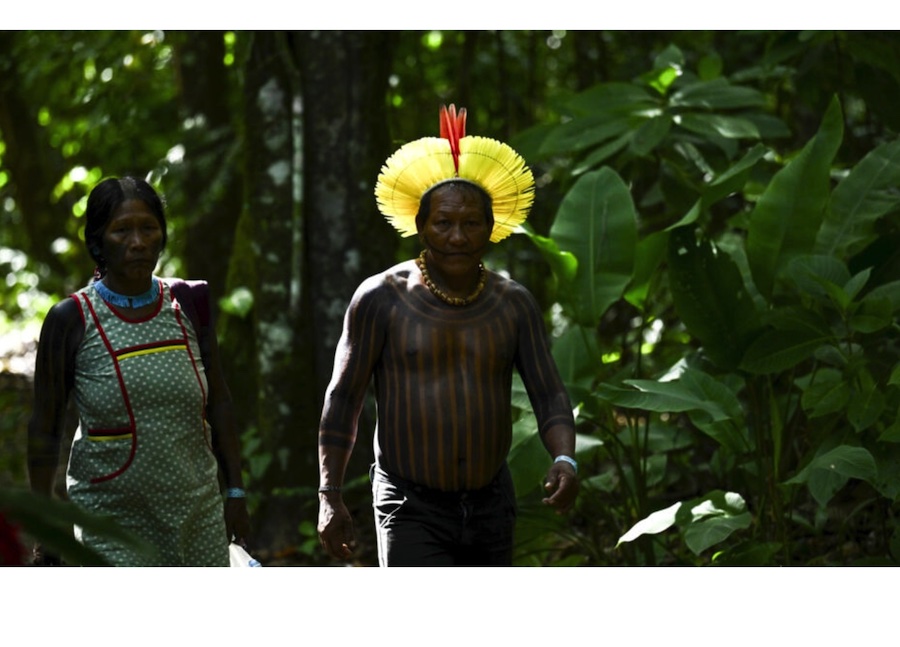

Indigenous groups call for bold steps at Amazon summit © Evaristo Sa / AFP
Instead, the joint declaration issued on Tuesday in the Brazilian city of Belem created an alliance for combating forest destruction, with countries left to pursue their own individual deforestation goals.
The failure of the eight Amazon countries to agree on a pact to protect their own forests points to the larger, global difficulties of forging an agreement to combat climate change. Many scientists say policymakers are acting too slowly to head off catastrophic global warming.
“The planet is melting, we are breaking temperature records every day. It is not possible that, in a scenario like this, eight Amazonian countries are unable to put in a statement – in large letters – that deforestation needs to be zero,” said Marcio Astrini of environmental lobby group Climate Observatory.
Lula and other national leaders left Tuesday’s meeting without commenting on the declaration. Presidents from Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia and Peru attended the summit, while Ecuador, Guyana, Suriname and Venezuela sent other top officials.
(article continued in right column)
Sustainable Development Summits of States, What are the results?
(Article continued from the left column)
Bolivia and Venezuela are the only Amazon countries not to sign onto a 2021 agreement among more than 100 countries to work toward halting deforestation by 2030. A Brazilian government source told Reuters in the lead up to the summit that Bolivia, where forest destruction is surging, is a hold-out on the issue.
Bolivian President Luis Arce did not address the 2030 commitment in his speech on Tuesday.
Brazil’s Foreign Minister Mauro Vieira said in a press briefing that the issue of deforestation “in no way whatsoever will divide the region” and cited “an understanding about deforestation” in the declaration, without elaborating.
This week’s summit brought together the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) for the first time in 14 years, with plans to reach a broad agreement on issues from fighting deforestation to financing sustainable development.
But tensions emerged in the lead up to the summit around diverging positions on deforestation and oil development.
Fellow Amazon countries also rebuffed Colombia’s leftist President Gustavo Petro’s ongoing campaign to end new oil development in the Amazon. In his speech on Tuesday, Petro likened the left’s desire to keep drilling for oil to the right-wing denial of climate science.
He said the idea of making a gradual “energy transition” away from fossil fuels was a way to delay the work needed to stop climate change.
Brazil is weighing whether to develop a potentially huge offshore oil find near the mouth of the Amazon River and the country’s northern coast, which is dominated by rainforest.
“What we are discussing in Brazil today is research of an extensive and large area – in my vision perhaps the last frontier of oil and gas before … the energy transition,” Brazil’s Energy Minister Alexandre Silveira told reporters after Petro’s speech.
Silveira said they should conduct research into what oil is there in order to make a decision on the issue.
Beyond deforestation, the summit also did not fix a deadline on ending illegal gold mining, although leaders agreed to cooperate on the issue and to better combat cross-border environmental crime.
The final joint statement, called the Belem Declaration, strongly asserted indigenous rights and protections, while also agreeing to cooperate on water management, health, common negotiating positions at climate summits, and sustainable development.
As Reuters previously reported, the declaration additionally established a science body to meet annually and produce authoritative reports on science related to the Amazon rainforest, akin to the United Nations’ International Panel on Climate Change.