. .. SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT .. .
A blog by Craig Morris in Energy Transition – The German Energiewende
Another setback for the “nuclear renaissance”: Switzerland voted on Friday to focus more on renewables and efficiency. For the first time ever, new nuclear plants are officially off the table—though admittedly, none were planned. The Swiss just “adopted the Energiewende,” writes the Neue Züricher Zeitung. Is no one paying attention? Craig Morris has the details.

The sun sets on the Leibstadt nuclear power plant, as seen from Dörflingen, Switzerland (Photo by Hansueli Krapf, edited, CC BY-SA 3.0)
(Click on image to enlarge)
Now here’s a news item you probably haven’t heard, at least judging from what I can gather on the internet: Switzerland’s new Energy Act (Energiegesetz, PDF) of 30 September 2016. You would think that, given its scope and Switzerland’s central role in Europe’s power sector, the following contents would have warranted a mention at, say, Reuters, CNN, Bloomberg, and Co.:
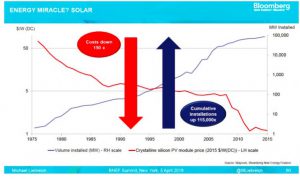
* The generation of non-hydro renewable power is to grow from 1.7 TWh last year (PDF in German and French) to 4.4 TWh by 2020 and 11.4 TWh by 2035 (nearly tenfold).
* “Per capita energy consumption” is to shrink by 16 percent from 2000 to 2020 and by 43 percent by 2035. “Per capita” is an important caveat in a small country whose population can easily grow quickly. (Switzerland’s is up around 10 percent over the past decade, like even smaller Norway’s.) Unfortunately, the law does not specify the most important aspect here: final or primary energy?
* Power consumption is to drop by 3 percent by 2020 and 13 percent by 2035.
* The law also, confusingly, speaks of “expanding” hydropower to 37.4 TWh by 2035 – even though it came in at 39.5 TWh last year. (If any readers know how to dissect this, please drop us a comment below.)
* It amends the 2003 Nuclear Energy Act (here’s the old one) to ban permits for new nuclear reactors. It also bans the reprocessing and export of spent fuel rods for reprocessing (except for research purposes with the consent of the Bundesrat). And “changes may not be made to existing nuclear plants.”
(Continued on right side of page)
Are we making progress in renewable energy?
Is there a future for nuclear energy?
(Article continued from left side of page)
There’s a lot more in the law, much of which deals with the policy mechanisms (level of feed-in tariffs, etc.). But what’s above is a real breakthrough. So why has it gone unreported in English?
One reason may be that a referendum could change everything, as the Swiss press explains (in German). But the report also suggests there is little support for such a referendum in industry, so the referendum may not even take place; in other words, the Swiss business world is happier with renewables and efficiency than with old-school energy production, consumption, and waste.
Another referendum will be held on 27 November 2016: the one for a closure of the existing reactors (in German). It does not necessarily stand a good chance of passing; parliamentarians overwhelmingly reject it (it’s an idea of the Swiss Greens). On the other hand, a recent survey of the public revealed support for a total phaseout by 2029 (basically, a limited service life of 45 years per reactor). This idea may have as much as 58 percent public support (in German)—possibly another example of politicians out of touch with the people. The first reactor to be shut down would then go offline in 2019. Leibstadt, the youngest, would be the last to go in 2029.
Opponents of the phaseout referendum will reportedly not try to reject the idea of a nuclear phaseout outright. Instead, they will try to win over the “silent majority” of undecided voters in the middle of the political spectrum by simply arguing that setting a specific date or service life for all reactors makes no sense. This clever tactic is likely to succeed, but a quick comparison with the historic debate in Germany over a nuclear phaseout suggests something less savory for nuclear supporters. Remember that slippery slope? By the time you resort to the tactic of “setting a date for a phaseout makes no sense,” you have reached the bottom of it. There is no way back up the slope for nuclear at that point.
Oddly, the Swiss press outlets all report that the new law is part of the government’s “Energy Strategy 2050” even though “2050” is never even mentioned in the new Act. This law is in fact just a starting point. By the end of this year, we will probably know what direction the country is headed.
One wonders when the international media will catch on. Maybe never—or did you know that Switzerland implemented a nuclear phaseout (by 2034) in the wake of Fukushima back in 2011?
Craig Morris (@PPchef) is the lead author of German Energy Transition. He is co-author of Energy Democracy, the first history of Germany’s Energiewende, and is currently Senior Fellow at the IASS.