DISARMAMENT & SECURITY .
An article by Aala Ali, Adham Hamed & Muntather Hassan from Impakter
“We heard children singing ISIL songs, and saw them role play executions in an Internally Displaced Persons (IDP) camp playground. We were distributing humanitarian aid. It was then that I realized, if we don’t do anything about this … a new, more extremist generation will be born,” Ziena, 27 years old.
Ziena graduated from one of six youth-training workshops hosted by UNDP Iraq partner, Iraqi Al-Amal Association, in 2018. Focused on preventing violent extremism (PVE) and conflict transformation, Ziena is one of 146 university students and youth activists who have been supported to carry out creative community-based activities in their universities and local communities.
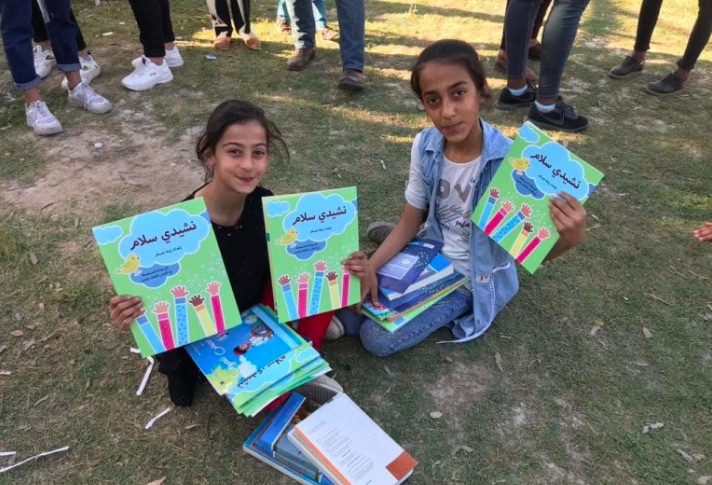

In the Photo: IDP Camp Children with Song Book. Photo Credit: Iraqi Al-Amal/2019
Struck by her own experience in an IDP Camp, Ziena created a children’s songbook; filled with words of peace and ideas that support a non- discriminative, gender equal, and non-violent future for Iraq. Each page of the book is decorated with the artwork of IDP children, which today, Ziena and her team of volunteers take to IDP camps to share. She hopes that music and song will guide these children toward a culture of peace and a future free from divisive ideologies.
But, whilst her story is heartwarming and her hands are those working to directly mend the hearts of conflict-affected communities, Ziena is addressing just one layer of conflict in Iraq’s peace-building process. She is instrumental in building a bridge between academic ideas and concepts required to frame a new culture of peace in Iraq, and the tangible actions made in her community, where she encounters survivors of conflict every day. Both aspects are necessary, and indeed complimentary, but there is another layer which is critical to ensuring sustainability of peace in Iraq — the structures that enable peace. For this, the active engagement of the government is crucial.
Recognizing the complexity of this task, the UNDP-funded project, Education for Peace in the Iraqi Higher Education System,” implemented by national NGO Iraqi Al-Amal Association and the UNESCO Chair for Peace Studies at the University of Innsbruck’s Unit for Peace and Conflict Studies, is designed to address all three levels of conflict — grass-roots, middle and high-level — through a combination of community level programming, curriculum development with the Iraqi Universities Consortium for Peace Studies and government engagement through the Ministry of Higher Education & Scientific Research (MOHESR).
Between October 2018 and March 2019, this culminated in the development of the first national Diploma for Peace and Conflict Studies, which will be piloted at the University of Baghdad later this year. Such an endeavor required an in-depth reflection about the potential meanings of peace and the impact of different notions of peace in the Iraqi context.
Defining Peace
UN Sustainable Development Goal 16 (SDG 16) calls for the promotion of peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development — providing justice for all and building effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels. In the same vein, on the International Day of Peace 2018, UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres stated, “There is more to achieving peace than laying down our weapons.”
Since wars begin in the minds of men, it is in the minds of men that the defenses of peace must be constructed.
So, what are the potential meanings of peace beyond the absence of war and direct violence? The preamble of the UNESCO constitution provides a helpful reference point: “Since wars begin in the minds of men, it is in the minds of men that the defenses of peace must be constructed.” Such an understanding of peace opens up a possibility to think about the idea of peace beyond a single universal notion that could be applied in all places and all times, regardless of the respective socio-political and cultural circumstances.
Wolfgang Dietrich, UNESCO Chairholder for Peace Studies at the University of Innsbruck, proposed the idea of “many peaces;” a concept that suggests that there are as many interpretations of peace as there are human beings in the world. This perspective provides an alternative avenue to universalist notions of how peace ought to be. By contrast it introduces a human-centered approach that puts people and the diversity of their lived experiences at the center of conflict transformation work. In the Iraqi context, which has long experienced external interventions, this makes the radical shift of agency to Iraqi citizens, who are now considered the central agents for formulating their own understandings of peace.
(Continued in right column)
Question related to this article:
A culture of peace in Iraq, Is it possible?
(Continued from left column)
Conflict and Violence in Iraq
From the first Gulf War and the authoritarian rule of Saddam Hussein, to the 2003 invasion, the subsequent 8-year Iraq war and ISIL’s occupation between 2014-2017, it is no surprise that the scars of war and conflict have marred the economic and social development potential of Iraq, despite its considerable oil resources. In 2017, according to the Institute for Economics and Peace, the economic impact of violence on the global economy was 14.76 trillion US Dollars or the equivalent of 12.4% of the global GDPBeyond Conflict Resolution
If it were the case that families, communities and societies could be fixed like the engine of a broken car, narrowly focusing on the material aspects of conflict might be a sufficient response. However, human relationships are more complex than the mechanistic qualities of an engine and they are not always rational, with messy human traits tied up in our experience, including crucial sexual, emotional, mental and spiritual dimensions that all constitute a part of human existence.
All of these aspects contribute to the tangible costs of conflict, and using short-term solutions alone to address them will only temporarily suppress conflict — with a strong likelihood that it will appear again, somewhere new. This is why, beyond the idea of simple conflict resolution, a more comprehensive approach to conflict transformation needs to put the relationships of people living and surviving in protracted conflicts at the center of a journey toward peaceful communities.
We know from experience that conflict transformation processes require years, decades or even generations, in the case of large-scale violence. The concept of the “200-years present,” first introduced by sociologist Elise Boulding, explains how an experience of violence will continue to resonate in subsequent generations, through the trans-generational dimensions of trauma. Which is why episodes of violence, such as those experienced during ISIL’s occupation of Iraq, will likely affect the relatives of survivors and witnesses for many years to come.
Hence, while immediate interventions for peace are necessary to address the material dimensions of conflict, such as reconstruction, it is equally crucial to consider the mid and long-term processes of relational work through trauma healing and peace education. This is not only much more cost-effective than investing in further securitization and militarization, but it also opens up the possibility for long-term change processes through the education sector, strengthened to provide platforms for peace. Peace education provides a possibility to think about “many peaces” and conflict transformation as a means of addressing personal and collective challenges that remain deeply ingrained in families, communities and societies moved by the experiences of war and violence. It’s an approach that in the spirit of the UNESCO Constitution starts with the human mind as a central resource for defending peace. And, from experience we know that this may not only contribute to the prevention of further outbreaks of direct violence but that it’s actually a means of transforming cultures of violence to cultures of peaces; equipping people with alternative and effective tools to transform their conflicts peacefully, such as dialogue, and mediation.
Peace education can also be used to help people develop their own ways of living and fostering cultures of peace, and to avoid the belief that their reality is directed by external forces. In Iraq there is a widespread belief that violent conflict is merely imposed by foreigners. This sense is built up from the community level and challenges the notion that people were living in peace before foreign intervention. Whilst we can recognise that there are many external factors contributing to instability in Iraq, we also see how this recognition is used as a strategy to avoid personal responsibility and agency, limiting the possibility of addressing conflict from within one’s own context. Avoiding agency frequently occurs as part of a denial phase after trauma. However, the inclusive, and elicitive approaches in peace education can facilitate ownership for Iraqis, enabling them to take forward this type of peace work and enhancing their level of responsibility on foundational issues.
A Catalyst for Change
The development of a national pilot curriculum for a “Diploma of Peace and Conflict Studies” is an intervention that has come after many years of armed conflict. At the beginning of this project, promoting peace education in the Iraqi higher education sector was the goal, but how can you continue academic life in a context marked by war, where lecture halls and libraries have been destroyed or burnt to the ground? And beyond material damage and destruction: How do you continue academic work and life in a meaningful way after experiencing the kind of atrocities that put all meaning of life into question?
Whilst the circumstances in post-ISIL Iraq are in many ways different from the political, cultural and social situation in Europe post-World War II, there are also certain parallels. Most strikingly we see a new-found momentum to establish a foundation of Peace and Conflict Studies as an academic discipline — and a recognition that the neighboring discipline of International Relations, founded after World War I, was largely unsuccessful in finding the answers to prevent genocide and the use of weapons of mass-destruction. This had a direct effect on the development of a broad range of applied conflict transformation methods, which have been of utmost use for transforming conflicts in a non-violent manner, and which, with the right methodologies, may achieve positive results in Iraq too. This consideration was at the heart of the “Education for Peace in the Iraqi Higher Education System” project. But why academia? Because Iraqi academics have collectively demonstrated a desire to actively contribute to national reconciliation, with a strong will to work together to address the questions of peace and conflict transformation through establishing Peace and Conflict Studies as a new discipline in Iraq.
This culminated in the formation of The Iraqi Universities Consortium for Peace Studies, between 2016-2017, with support from Iraqi Al-Amal, UNDP Iraq and Eastern Mennonite University. The Consortium — comprised of academics from the Universities of Baghdad, Tikrit, Anbar, Basra, Karbala, Kufa and Mosul — became a vocal advocate for the development of Peace Studies in a post-conflict Iraq and actively participated in capacity building activities to train academics and in-turn contribute to the development of a context appropriate curriculum.