… . HUMAN RIGHTS … .
Annual report of Amnesty International
* Amnesty International’s Annual Report for 2022 highlights double standards throughout the world on human rights and the failure of the international community to unite around consistently-applied human rights and universal values.
* The West’s robust response to Russia’s aggression against Ukraine contrasts sharply with a deplorable lack of meaningful action on grave violations by some of their allies including Israel, Saudi Arabia and Egypt.
* Women’s rights and freedom to protest are threatened as states fail to protect and respect rights at home.
* As the Universal Declaration of Human Rights turns 75, Amnesty International insists that a rules-based international system must be founded on human rights and applied to everyone, everywhere.

Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine in 2022 unleashed numerous war crimes, generated a global energy and food crisis and sought to further disrupt a weak multilateral system. It also laid bare the hypocrisy of Western states that reacted forcefully to the Kremlin’s aggression but condoned or were complicit in grave violations committed elsewhere, Amnesty International said as it launched its annual assessment of human rights around the world.
Amnesty International Report 2022/23: The State of the World’s Human Rights found that double standards and inadequate responses to human rights abuses taking place around the world fuelled impunity and instability, including deafening silence on Saudi Arabia’s human rights record, inaction on Egypt and the refusal to confront Israel’s system of apartheid against Palestinians.
The report also highlights China’s use of strong-arm tactics to suppress international action on crimes against humanity it has committed, as well as the failure of global and regional institutions – hamstrung by the self-interest of their members – to respond adequately to conflicts killing thousands of people including in Ethiopia, Myanmar and Yemen.
“Russia’s invasion of Ukraine is a chilling example of what can happen when states think they can flout international law and violate human rights without consequences,” said Agnès Callamard, Amnesty International’s Secretary General.
“The Universal Declaration of Human Rights was created 75 years ago, out of the ashes of the Second World War. At its core is the universal recognition that all people have rights and fundamental freedoms. While global power dynamics are in chaos, human rights cannot be lost in the fray. They should guide the world as it navigates an increasingly volatile and dangerous environment. We must not wait for the world to burn again.”
Shameless double standards pave way for further abuses
Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine triggered one of Europe’s worst humanitarian and human rights emergencies in recent history. The conflict not only resulted in mass displacement, war crimes and global energy and food insecurity, it also raised the chilling spectre of nuclear war.
The response was swift with the West imposing economic sanctions on Moscow and sending military assistance to Kyiv, the International Criminal Court opening an investigation into war crimes in Ukraine and the UN General Assembly voting to condemn Russia’s invasion as an act of aggression. However, this robust and welcomed approach stood in stark contrast to previous responses to massive violations by Russia and others, and to pitiful existing responses on conflicts such as Ethiopia and Myanmar.
“Had the system worked to hold Russia accountable for its documented crimes in Chechnya and Syria, thousands of lives might have been saved then and now, in Ukraine and elsewhere. Instead, what we have is more suffering and devastation,” said Agnès Callamard.
“If Russia’s war of aggression demonstrates anything for the world’s future, it is the importance of an effective and consistently applied rules-based international order. All States must step up their efforts for a renewed rules-based order that benefits everyone, everywhere.”
For Palestinians in the occupied West Bank, 2022 was one of the deadliest years since the UN began systematically recording casualties in 2006, with at least 151 people, including dozens of children, killed by Israeli forces. Israeli authorities continued to force Palestinians from their homes, and the government is rolling out plans to drastically expand illegal settlements across the occupied West Bank. Instead of demanding an end to Israel’s system of apartheid, many Western governments chose to attack those denouncing it.
The USA has been a vocal critic of Russian violations in Ukraine and has admitted tens of thousands of Ukrainians fleeing the war, yet under policies and practices rooted in anti-Black racism, it expelled more than 25,000 Haitians between September 2021 and May 2022, and subjected many to torture and other ill-treatment.
EU member states opened their borders to Ukrainians fleeing Russian aggression, demonstrating that, as one of the richest blocs in the world, they were more than capable of receiving large numbers of people seeking safety and giving them access to health, education and accommodation. However, many kept their doors shut to those escaping war and repression in Syria, Afghanistan and Libya.
“Responses to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine gave us some evidence of what can be done when there is political will. We saw global condemnation, investigations of crimes, borders opened to refugees. This response must be a blueprint for how we address all massive human rights violations,” said Agnès Callamard.
The West’s double standards emboldened countries like China, and enabled Egypt and Saudi Arabia to evade, ignore and deflect criticism of their human rights record.
Despite massive human rights violations, amounting to crimes against humanity against Uyghur and other Muslim minorities, Beijing escaped international condemnation by the UN General Assembly, Security Council and Human Rights Council.
The UN Human Rights Council established a Special Rapporteur on the human rights situation in Russia and an investigative mechanism on Iran in the wake of deadly protests. But it voted not to further investigate or even discuss the UN’s own findings of potential crimes against humanity in Xinjiang, China, and discontinued a resolution on the Philippines.
“Countries applied human rights law on a case-by-case basis in a staggering show of blatant hypocrisy and double standards. States cannot criticize human rights violations one minute and, in the next, condone similar abuses in other countries just because their interests are at stake. It’s unconscionable and undermines the entire fabric of universal human rights,” said Agnès Callamard.
(Article continued in right column)
(Click here for the French version of this article, or here for the Spanish version .)
Question(s) related to this article:
What is the state of human rights in the world today?
(Article continued from left column)
“We also need States that have so far failed to put their head above the parapet to take a stand against human rights abuses wherever they fall. We need less hypocrisy, less cynicism, and more consistent, principled and ambitious action by all states to promote and protect all rights.”.
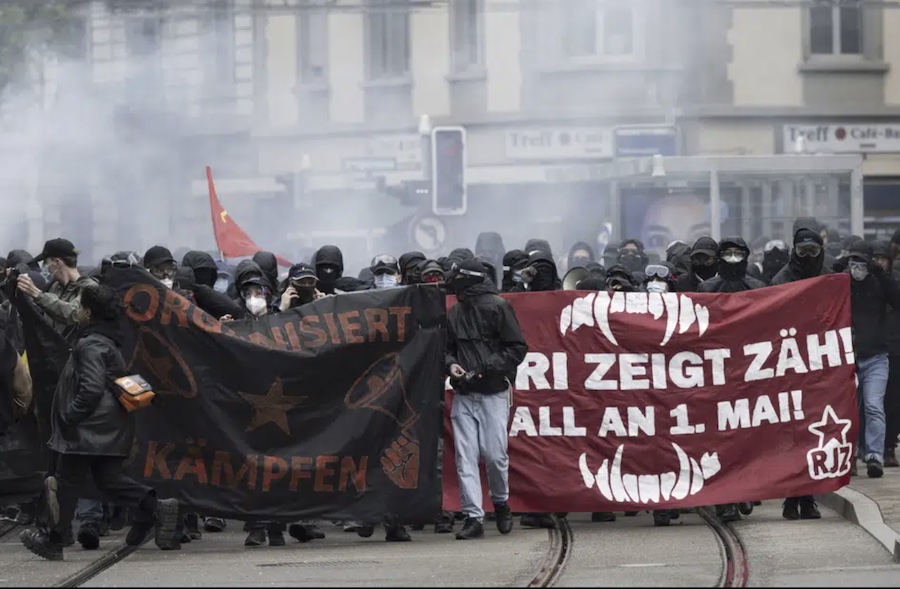
Ruthless repression of dissent across the world
In 2022, Russian dissenters were taken to court and media houses were shut down just for mentioning the war in Ukraine. Journalists were imprisoned in Afghanistan, Ethiopia, Myanmar, Russia, Belarus and dozens of other countries across the world where conflicts raged.
In Australia, India, Indonesia and the UK, authorities passed new legislation imposing restrictions on demonstrations while Sri Lanka used emergency powers to curtail mass protests against the spiralling economic crisis. The UK law gives police officers wide-ranging powers, including the ability to ban “noisy protests”, undermining the freedoms of expression and peaceful assembly.
Technology was weaponized against many, to silence, prevent public assembly or disinform.
Iranian authorities responded to the unprecedented uprising against decades of repression with unlawful force through live ammunition, metal pellets, tear gas and beatings. Hundreds of people, including dozens of children, were killed. In December, Peruvian security forces used unlawful force, especially against indigenous people and campesinos, to quell protests during the political crisis that followed the ousting of former president Castillo. Journalists, human rights defenders and political opposition also faced repression including in Zimbabwe and Mozambique.
In response to growing threats to the right to protest, Amnesty International launched a global campaign in 2022 to confront states’ intensifying efforts to erode the fundamental right to freedom of peaceful assembly. As part of this campaign the organization calls for the adoption of a Poland were prosecuted for helping women access abortion pills.
Indigenous women continued to face disproportionately high levels of rape and other sexual violence in the USA. In Pakistan, several high-profile murders of women by family members were reported yet parliament failed to adopt legislation on domestic violence that had been pending since 2021. In India, violence against Dalit and Adivasi women, among other caste-based hate crimes, was committed with impunity.
Afghanistan witnessed a particularly significant deterioration of women and girls’ rights to personal autonomy, education, work, and access to public spaces, through multiple edicts issued by the Taliban. In Iran, the “morality police” violently arrested Mahsa (Zhina) Amini for showing strands of hair under her headscarf, and days later she died in custody amid credible reports of torture, sparking nationwide protests in which many more women and girls were injured, detained or killed.
“States’ hunger to control the bodies of women and girls, their sexuality and their lives leaves a terrible legacy of violence, oppression and stunted potential,” said Agnès Callamard.
A crowd of protesters proceeds over the Brooklyn Bridge with the New York skyline in the background. They carry a large banner with the words ‘my body my choice’.
Global action against threats to humanity woefully inadequate
In 2022, the world continued to suffer the fall-out of the Covid-19 pandemic. Climate change, conflict and economic shocks caused in part by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine further compounded the risks to human rights.
Economic crises meant 97% of the population of Afghanistan were living in poverty. In Haiti, the political and humanitarian crisis, exacerbated by widespread gang violence, left more than 40% of the population facing acute food insecurity.
Extreme weather conditions exacerbated by a rapidly warming planet triggered hunger and disease in several countries in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, including Pakistan and Nigeria where floods had a catastrophic impact on people’s lives and livelihoods and led to an outbreak of waterborne diseases, which killed hundreds.
Against this backdrop, countries failed to act in the best interests of humanity and address fossil fuel dependency, the main driver pushing us toward the biggest threat to life as we know it. This collective failure was another stark example of the weakness of current multilateral systems.
“The world is besieged by an onslaught of colliding crises including widespread conflict, cruel global economics with too many states burdened by unsustainable debt, corporate tax abuse, the weaponization of technology, the climate crisis and shifting tectonic plates of power. We stand no chance of surviving these crises if our international institutions aren’t fit for purpose,” said Agnès Callamard.
Dysfunctional international institutions need fixing
It is vital that international institutions and systems that are meant to protect our rights are strengthened rather than undermined. The first step is for UN human rights mechanisms to be fully funded, so that accountability and investigations can be pursued, and justice delivered.
Amnesty International is also calling for the UN’s key decision-making body, the Security Council, to be reformed to give a voice to countries and situations which have been traditionally ignored, especially in the global south.
“The international system needs serious reform to reflect the realities of today. We cannot allow the permanent members of the UN Security Council to continue wielding their veto power and abusing their privileges unchecked. The lack of transparency and efficiency in the Council’s decision-making process leaves the entire system wide open to manipulation, abuse and dysfunction,” said Agnès Callamard.
But while self-serving governments fail to put our human rights first, the human rights movement shows we can still draw inspiration and hope from the people these states should have protected.
In Colombia, the persistence of women’s rights activism and legal action contributed to the Constitutional Court’s decision to decriminalize abortion during the first 24 weeks of pregnancy. In South Sudan, Magai Matiop Ngong was released from prison, having been sentenced to death at the age of 15 in 2017. His release came after thousands of people around the world petitioned the authorities for his freedom.
Indigenous Mayan environmentalist Bernardo Caal Xol was released on parole after spending four years in jail in Guatemala on bogus charges. After years of campaigning by women’s movements in Spain, the country’s parliament passed a law placing consent at the centre of the legal definition of rape. Kazakhstan and Papua New Guinea repealed the death penalty.
“It is easy to feel hopeless in the face of atrocities and abuses but throughout the last year, people have shown we are not powerless,” said Agnès Callamard.
“We’ve witnessed iconic acts of defiance, including Afghan women marching against Taliban rule and Iranian women walking unveiled in public or cutting their hair to protest compulsory veiling laws. Millions of people who have been systematically oppressed by patriarchy and racism took to the streets to demand a better tomorrow. They did so in previous years and they did so again in 2022. This should remind those in power that we will never be mere bystanders when they assault our dignity, equality and freedom.”
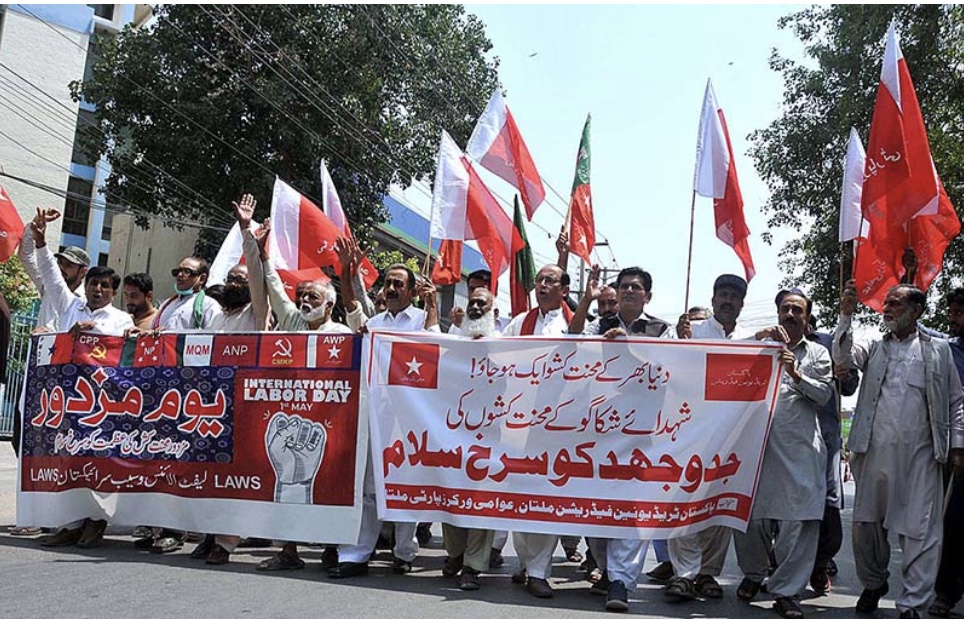
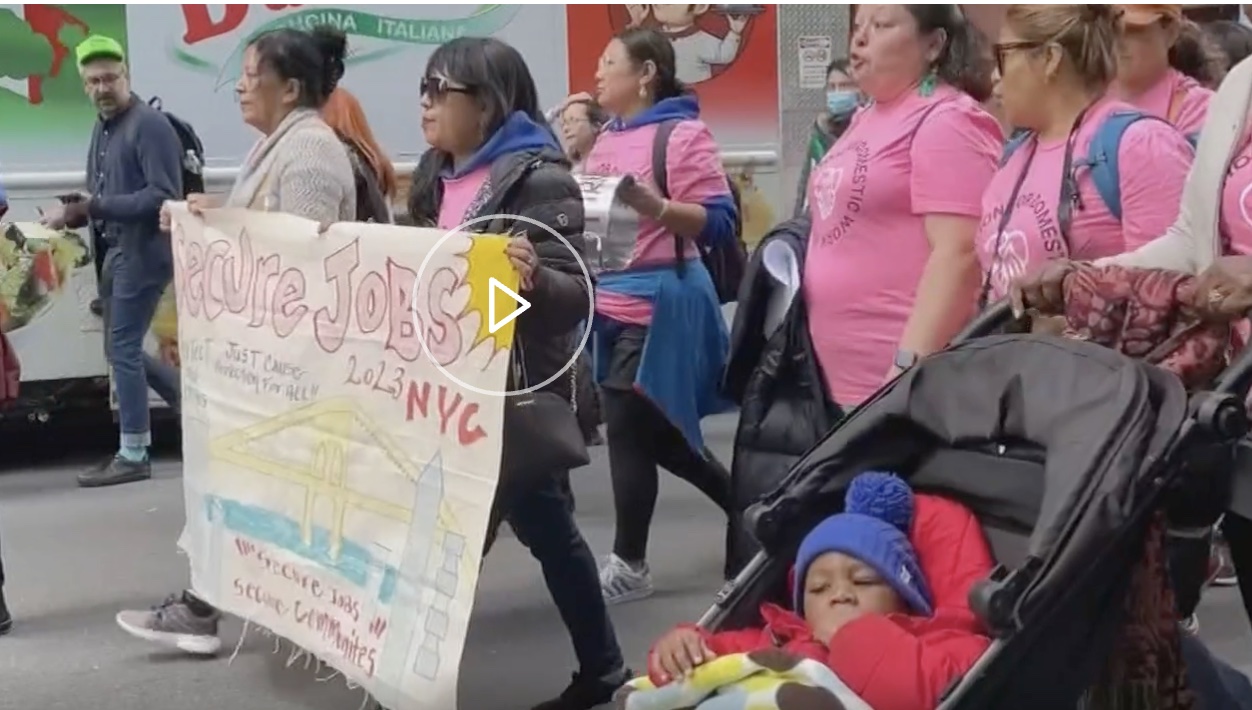
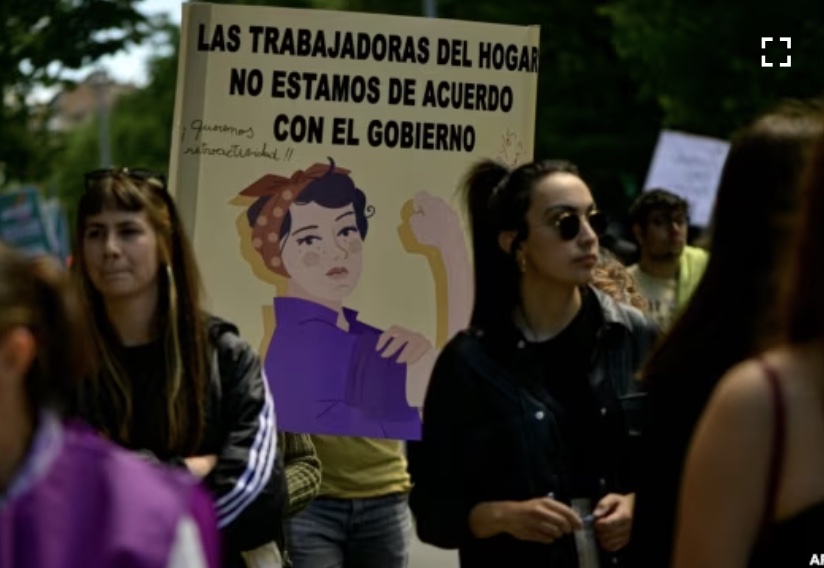
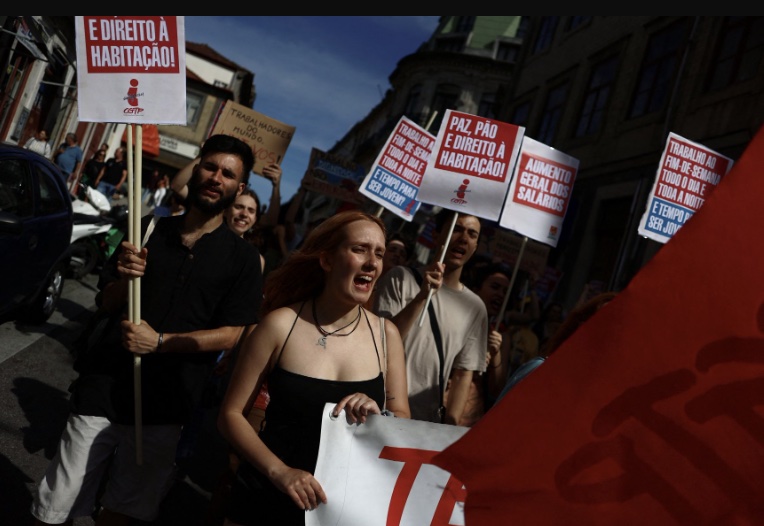
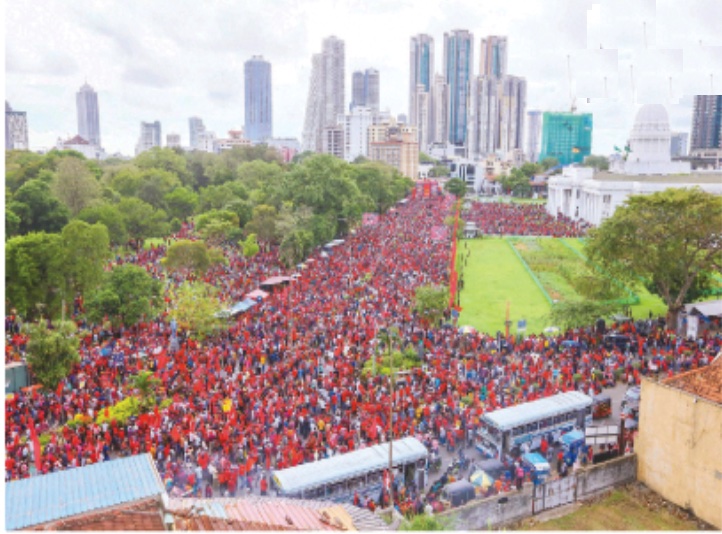
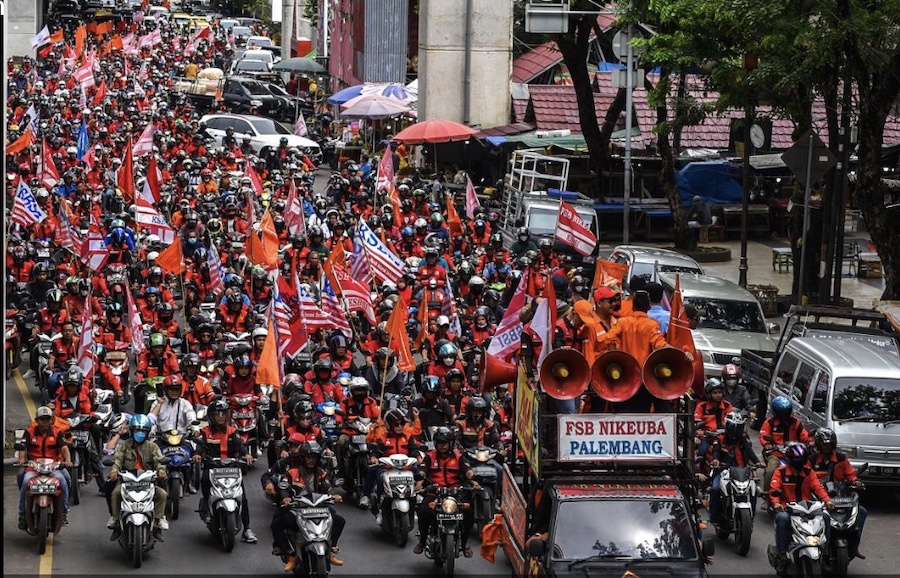































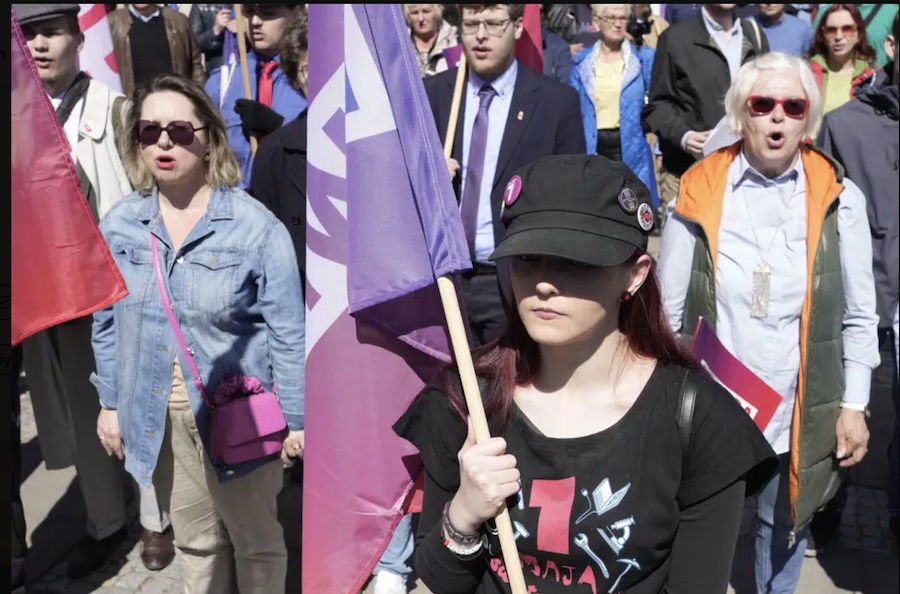
 Labour day parade march in front of the town hall in Vienna, Austria. [Lisa Leutner/AP Photo]
Labour day parade march in front of the town hall in Vienna, Austria. [Lisa Leutner/AP Photo]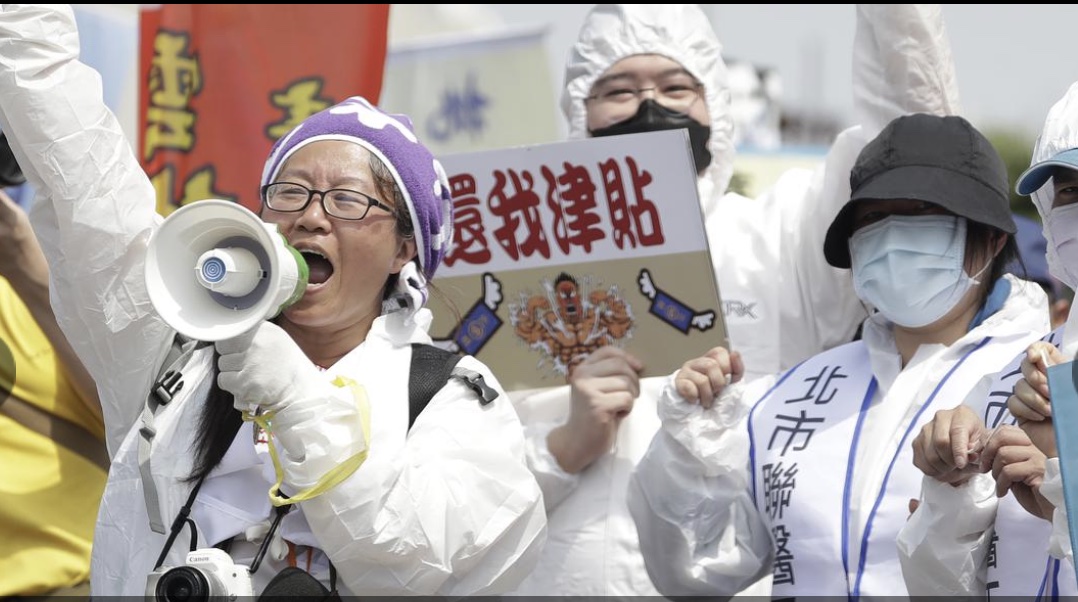 Medics hold slogans reading “I want benefits” during a May Day rally in Taipei, Taiwan (AP Photo/Chiang Ying-ying)
Medics hold slogans reading “I want benefits” during a May Day rally in Taipei, Taiwan (AP Photo/Chiang Ying-ying)