DISARMAMENT & SECURITY .
A speech by Yurii Sheliazhenko published by World Beyond War
Yurii Sheliazhenko, a Board Member of World BEYOND War, gave this speech at the webinar of the International Peace Bureau “365 Days of War in Ukraine: Prospects Towards Peace in 2023” (24 February 2023)
Dear friends, greetings from Kyiv, capital of Ukraine.
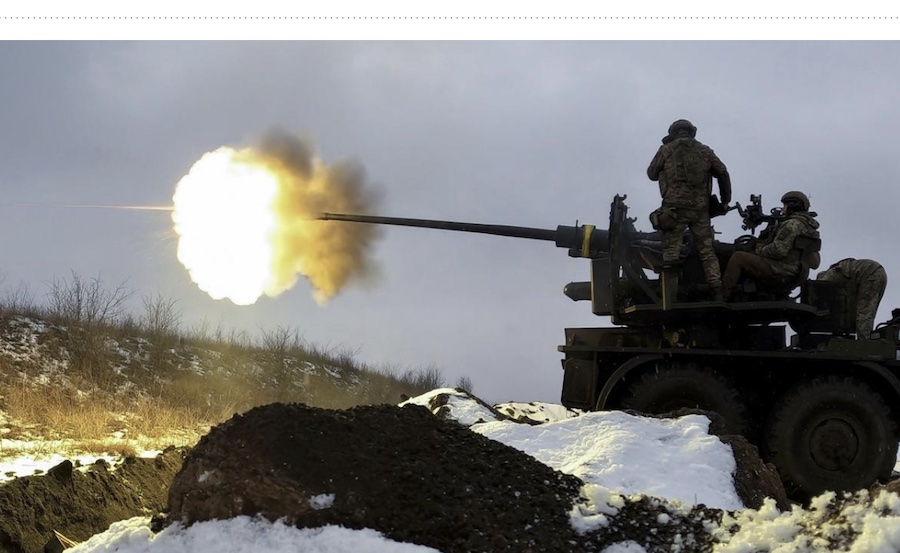
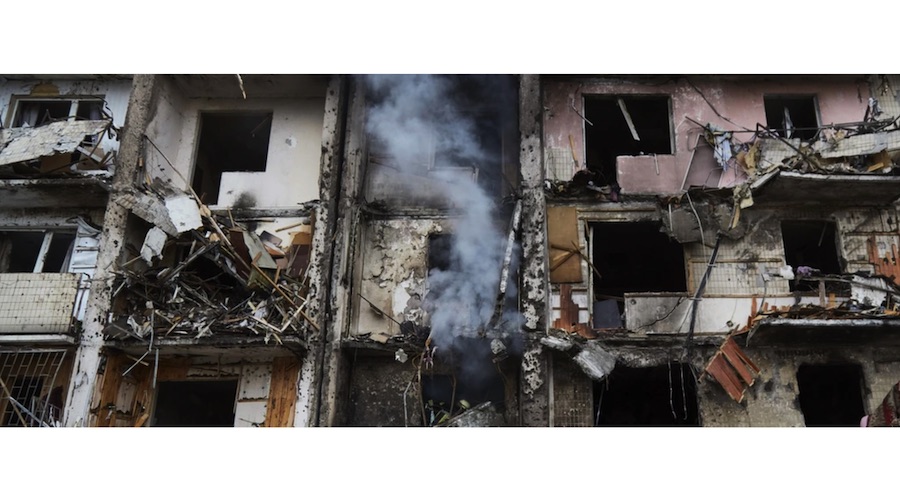
We meet today on the disgusting anniversary of the beginning of a full scale Russian invasion, which brought to my country enormous killing, suffering and destruction.
All these 365 days I lived in Kyiv, under Russian bombing, sometimes without electricity, sometimes without water, as many other Ukrainians who were lucky to survive.

I heard explosions behind my windows, my home shaked from pounding of artillery in distant combat.
I was disappointed by the failures of Minsk agreements, of peace talks in Belarus and Türkiye.
I saw how Ukrainian media and public spaces became more obsessed with hatred and militarism. Even more obsessed, than previous 9 years of armed conflict, when Donetsk and Luhansk were bombed by the Ukrainian army, like Kyiv was bombed by the Russian army during last year.
I called for peace openly despite threats and insults.
I demanded ceasefire and serious peace talks, and especially insisted on the right to refuse to kill, in online spaces, in letters to Ukrainian and Russian officials, calls to civil societies, in nonviolent actions.
My friends and colleagues from the Ukrainian Pacifist Movement did the same.
Because of closed borders and cruel hunting for draftees at the streets, in transport, in hotels and even in churches — we, Ukrainian pacifists, had no choice but to call for peace directly from the battlefield! And it is not an exaggeration.
One of our members, Andrii Vyshnevetsky, was conscripted against his will and sent to the frontline. He asks for discharge on the grounds of conscience in vain because the Armed Forces of Ukraine refused to respect human right to conscientious objection to military service. It is penalized, and we already have prisoners of conscience such as Vitalii Alexeienko who said, before the police took him to prison for his refusal to kill: “I will read New Testament in Ukrainian and I will pray for God’s mercy, peace and justice for my country.”
Vitaliy is a very brave man, he so courageously went to suffer for his faith without any attempts to escape or evade prison, because clear conscience gives him a feeling of security. But such sort of believers are rare, most people think about security in pragmatic terms, and they are right.`
To feel secure, your life, health and wealth must not be in danger, and there must be no worries for family, friends and your whole habitat.
People used to think that national sovereignty with all might of armed forces protects their safety from violent intruders.
Today we hear a lot of loud words about sovereignty and territorial integrity. They are key words in the rhetoric of Kyiv and Moscow, Washington and Beijing, other capitals of Europe, Asia, Africa, America and Oceania.
President Putin wages his war of aggression to protect the sovereignty of Russia from NATO on the doorstep, the tool of U.S. hegemony.
President Zelensky asks and receives from NATO countries all sorts of deadly weapons to defeat Russia which, if not defeated, is perceived as a threat for Ukrainian sovereignty.
Mainstream media wing of military industrial complexes convince people that the enemy is non-negotiable if not crushed before negotiations.
(Continued in right column)
Can the peace movement help stop the war in the Ukraine?
How can just one or a few persons contribute to peace and justice?
(Continued from left column)
And people believe that sovereignty protects them from war of all against all, in the words of Thomas Hobbes.
But the world of today is different from the world of Westphalian peace, and the feudal notion of sovereignty and territorial integrity don’t address brazen human rights violations committed by all sorts of sovereigns by war, by fake democratic warmongering, and by open tyranny.
How many times have you heard about sovereignty and how many times you heard about human rights?
Where we lost human rights, repeating the mantra about sovereignty and territorial integrity?
And where did we lost common sense? Because the more powerful army you have, the more fear and resentment it causes, turning friends and neutrals into enemies. And no army can avoid battle for a long time, it is eager to shed blood.
People must understand that they need nonviolent public governance, not belligerent sovereignty.
People need social and environmental harmony, not autarchic territorial integrity with militarized borders, barbed wire and gunned men waging war on migrants.
Today the blood is shedding in Ukraine. But current plans to wage the war for years and years, for decades, may turn the whole planet into a battlefield.
If Putin or Biden feel secure sitting on their nuclear stockpiles, I am scared of their security and millions of sane people are scared too.
In a rapidly polarizing world, the West decided to see security in war profiteering and fueling the war machine by arms deliveries, and the East chose to take by force what he sees as its historical territories.
Both sides have so-called peace plans to secure all they want in an extremely violent manner and then make the other side accept new power balance.
But it is not a peace plan to defeat the enemy.
It is not a peace plan to take contested land, or remove representatives of other cultures from your political life, and negotiate on conditions of acceptance of this.
Both sides apologize their warmongering behavior claiming that sovereignty is at stake.
But what I must say today: a more important thing than sovereignty is at stake today.
Our humanity is at stake.
Ability of humankind to live in peace and resolve conflicts without violence is at stake.
Peace is not eradication of the enemy, it is making friends from enemies, it is remembering of universal human brotherhood and sisterhood and universal human rights.
And we must admit that governments and rulers of the East and West are corrupted by military industrial complexes and by great power ambitions.
When governments are unable to build peace, it is on us. It is our duty, as civil societies, as peace movements.
We must advocate ceasefire and peace talks. Not only in Ukraine, but everywhere, in all endless wars.
We must uphold our right to refuse to kill, because if all people refuse to kill there will be no wars.
We must learn and teach practical methods of peaceful life, nonviolent governance and conflict management.
On examples of restorative justice and widespread replacement of litigation with mediation we see progress of nonviolent approaches to justice.
We can achieve justice without violence, as Martin Luther King said.
We must build an ecosystem of peacebuilding in all spheres of life, alternative to toxic militarized economy and politics.
This world is sick with endless wars; let’s say this truth.
This world must be healed with love, knowledge and wisdom, by rigorous planning and peace action.
Let’s heal the world together.