. . WOMEN’S EQUALITY . .
An article from the United Nations
New goals and effective plans on women’s involvement in peacebuilding are needed before it is too late, the head of the UN agency leading global efforts to achieve gender equality warned the Security Council on Tuesday.
Sima Bahous, Executive Director of UN Women, was speaking during a Council meeting to reaffirm the importance of Resolution 1325 on women, peace and security, adopted in October 2000, and to take stock of implementation since it turned 20 nearly three years ago.
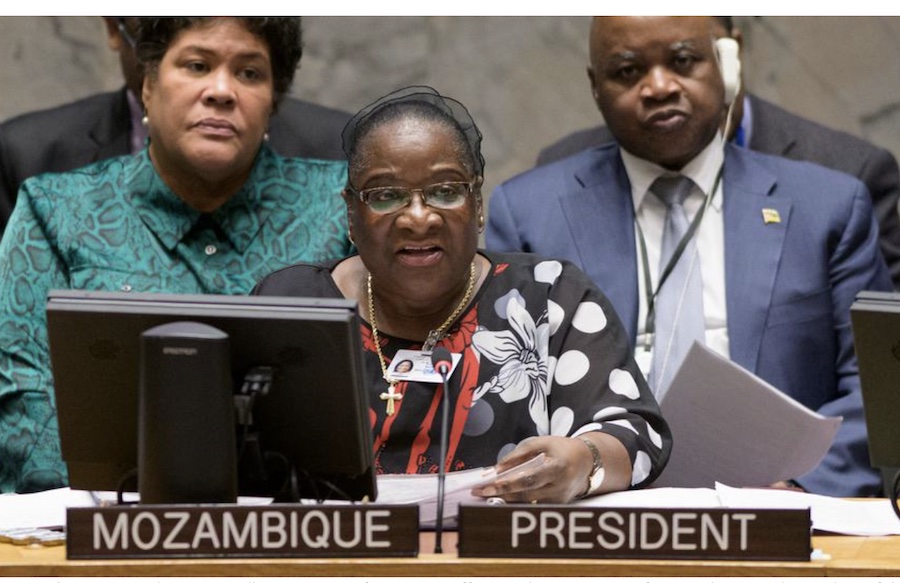

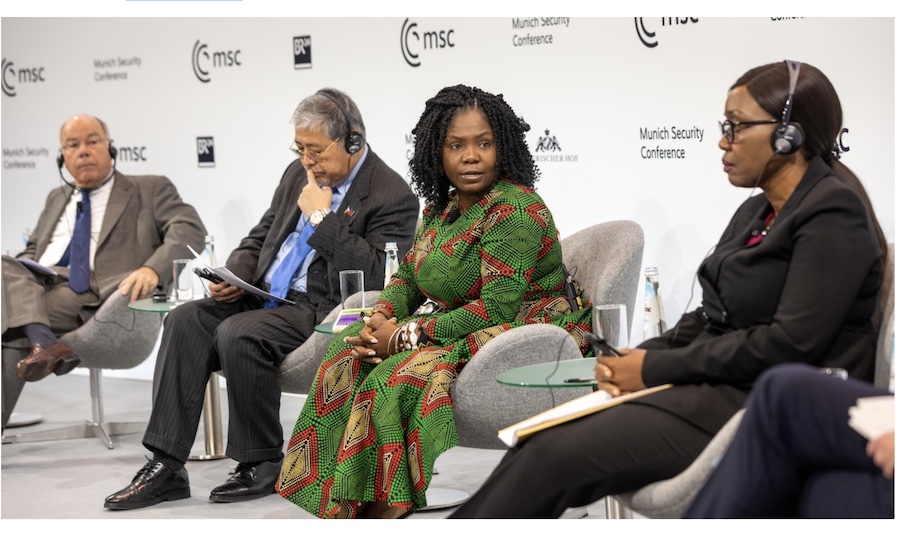
UN Photo/Manuel Elías Verónica Nataniel Macamo Dlhovo, Minister for Foreign
Affairs and Cooperation of Mozambique and President of the Security Council
for the month of March, chairs the Security Council meeting on
Women and peace and security.
“As we meet today at the mid-point between the 20th and 25th anniversaries, on the eve of International Women’s Day, it is obvious that we need a radical change of direction,” she said.
No significant change
Ms. Bahous noted that although several historic firsts for gender equality occurred during the first two decades of the resolution, “we have neither significantly changed the composition of peace tables, nor the impunity enjoyed by those who commit atrocities against women and girls.”
She said the 20th anniversary “was not a celebration, but a wake-up call,” pointing to situations from across the globe that have emerged since then.
They include the regression of women’s and girls’ rights in Afghanistan in the wake of the Taliban takeover, sexual violence committed in the war in the Tigray region in Ethiopia, and online abuse targeting women opposing military rule in Myanmar.
Women and children also comprise a staggering 90 per cent of the nearly eight million people forced to flee the conflict in Ukraine, and nearly 70 per cent of those displaced within the country.
Military spending increasing
Furthermore, women peacebuilders had hoped that the COVID-19 pandemic would cause countries to rethink military spending, as the global crisis revealed the value of caregivers and the importance of investing in health, education, food security and social protection.
“Instead, that spending has continued to grow, passing the two-trillion-dollar mark, even without the significant military expenditure of the last months,” she said. “Neither the pandemic nor supply-chain issues prevented another year of rising global arms sales.”
The way forward
Ms. Bahous outlined two suggestions that show what a change of direction could look like for the international community.
“First, we cannot expect 2025 to be any different if the bulk of our interventions continue to be trainings, sensitization, guidance, capacity building, setting up networks, and holding one event after another to talk about women’s participation, rather than mandating it in every meeting and decision-making process in which we have authority,” she stipulated.
Her second point focused on the need to get resources to women’s groups in conflict-affected countries, particularly through the Women’s Peace and Humanitarian Fund.
The UN-led partnership was established in 2015 and has so far supported more than 900 organizations.
“We urgently need better ways to support civil society and social movements in these countries. That means being much more intentional about funding or engaging with new groups, and especially with young women,” she said.
(Article continues in right column.)
UN Resolution 1325, does it make a difference?
Does the UN advance equality for women?
Can the women of Africa lead the continent to peace?
(Article continued from left column.)
Women’s involvement equals success
The meeting was chaired by Mozambique, which holds the rotating Security Council presidency this month.
The country’s Foreign Minister, Verónica Nataniel Macamo Dlhovo, expressed hope that the debate will lead to action, such as stronger strategies on gender equality, as well as women’s effective participation in peacekeeping and peacebuilding.
“There is no doubt that by involving women in the peacebuilding and peacekeeping agenda in our countries, we will achieve success,” she said, speaking in Portuguese.
“Under no circumstances do we want that the people who bring life into the world are negatively impacted. We must protect them. Use women’s sensitivity to resolve conflicts and maintain peace on our planet.”
Respect international law
Currently, more than 100 armed conflicts are raging around the world, according to Mirjana Spoljaric, President of the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC).
The organization sees the daily brutal impacts of armed conflict on women and girls, she said, which include “shocking levels” of sexual violence, displacement, and deaths during childbirth because they lack access to care.
Ms. Spoljaric upheld the importance of international humanitarian law during conflict and urged States to apply a gender perspective in its application and interpretation.
“Respect for international humanitarian law will prevent the enormous harm resulting from violations of its rules, and it will help to rebuild stability and reconcile societies,” she said.
States also must ensure that the clear prohibition of sexual violence under international humanitarian law is integrated into national law, military doctrine and training.
“Engaging more boldly and directly weapon bearers on this issue – with the ultimate goal that it does not occur in the first place – should become a de facto preventive approach, supported and facilitated in times of peace to prevent the worst in times of war,” she added.
African women leaders network
Bineta Diop of the African Union Commission also addressed the Council, highlighting its work in getting countries to accelerate implementation of the resolution.
This is being done through a strategy focused on advocacy and accountability, and in building a network of women leaders on the continent.
“We are ensuring that women’s leadership is mainstreamed in governance, peace and development processes so as to create a critical mass of women leaders at all levels,” she said.
“We need to make sure that they are in all sectors of life. not just in peace processes.”
Partner with women activists
Nobel Peace Prize winner Leymah Gbowee from Liberia called for amplifying the women, peace and security agenda. She recommended steps such as engaging and partnering with local women peace activists, who she called “the custodians of their communities.”
Women must also be negotiators and mediators in peace talks. “It is amazing to see how only the men with guns are consistently invited to the table to find solutions, while women who bear the greatest brunt are often invited as observers,” she remarked.
She also urged countries to “move beyond rhetoric” by ensuring funding and political will, because without them, Resolution 1325 “remains a toothless bulldog”.
Ms. Gbowee stressed that women, peace and security must be seen as a holistic part of the global peace and security agenda.
“We will continue to search for peace in vain in our world unless we bring women to the table,” she warned. “I firmly believe that trying to work for global peace and security minus women is trying to see the whole picture with your one eye covered.”