. . SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT . .
Excerpts from the website of Go Fossil Free
As the world wakes up to urgency of keeping global warming below 1.5C, a major milestone has been reached in the worldwide movement to stop investments in the fossil fuel companies driving the climate crisis. Over 1000 institutions with managed investments worth almost USD $8 trillion have committed to divest from fossil fuels.
Since 2012 the number of institutions commiting to fossil fuel divestment has increased rapidly and spread globally. From 181 institutions and $50 billion worth of assets committed to divestment at the end of 2014, to almost $8 trillion today.
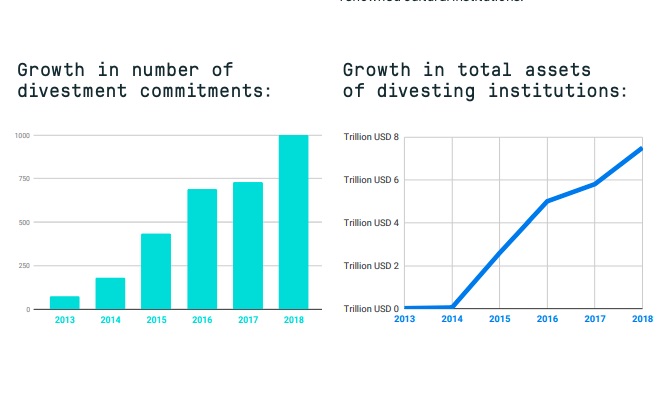
The reach and impact of this new global movement is huge, major institutions committing to remove, in whole or in part, nearly $8 trillion in assets from fossil fuel investments. The momentum has been driven by a people-powered grassroots movement, ordinary people on every continent pushing their local institutions to take a stand against the fossil fuel industry and for a world powered by 100% renewable energy.
In the financial world, divestment has taken on a momentum of its own as well. Fund managers and fiduciaries are increasingly aware of the risks of climate breakdown and deciding of their own accord to divest from morally unsound and financially risky industries.
The 1000th institution to divest is the Caisse des dépôts et consignations (CDC), which manages France’s public sector pensions, savings, and investments worth €173 billion (USD $196 billion). It recently announced that from 2019 it will no longer invest in companies that generate more than 10% of their business from coal. . . .
(continued in right column)
Divestment: is it an effective tool to promote sustainable development?
(continued from left column)
What started as a trickle of early divestment announcements from pioneering progressive institutions like the Quakers and a small number of universities has now swept up some of the world largest pension funds and insurers, dozens of world-class universities, the world’s largest sovereign wealth funds, the country of Ireland, major capital cities, as well as philanthropic foundations, health associations and worldrenowned cultural institutions. . . .
The impact
While some continue to dismiss divestment, arguing it will have no discernible impact on the bottom line of fossil fuel companies, they miss the point of the movement entirely — Our theory of change is two fold:
1. Create an opportunity for millions of people to get directly involved in challenging the drivers of climate breakdown
2. Stigmatise the fossil fuel industry and reduce its power over politicians and climate policy. We measure how well the Fossil Free campaign is doing not only by the amount of money divested from any particular oil company.
We measure success by how publicly an institutions makes its Fossil Free commitments, by how many activists are taking action online and in the streets and by how socially acceptable it is to invest in or be publicly associated with the reckless fossil fuel industry.
When institutions as diverse as the British Medical Association, Caisse des Dépôts et Consignations (the French public financial institution), New York City, Capetown, the World Council of Churches, the Rockefeller Brothers Fund, Stockholm University, Tate Britain museums and Allianz Insurance all turn their backs on the fossil fuel industry, the signals are starting to get through loud and clear to a wide-cross section of society.
Fossil fuel companies have never had a worse reputation or been more on the defensive than today. Solar power, wind energy, tidal, geothermal and advances in battery storage and hydroenergy are leaping ahead of antiquated fossil fuels like coal and tarsands in terms of affordability, popular public support, and cost-effectiveness per kilowatt hour. The success and profile of the divestment movement has created the space for governments to advance climate policy and legislation, and in some cases to go further and directly challenge fossil fuel companies through litigation.