|
|
Germany Makes Progress in Shift from Nuclear to Renewable Energy
un article par OECD Reviews: Germany 2012
[Editor's Note: Germany has taken the lead among advanced economies in deciding to eliminate nuclear power plants. For environmental sustainability it is important that they increase the use of renewable energy sources, as detailed in this OECD report.]
This OECD Environmental Performance Review provides an independent assessment of Germany’s progress in achieving domestic and international environmental policy commitments, together with policy relevant recommendations. It has been conducted to promote peer learning, to enhance countries’ accountability to each other and to the public, and to improve governments’ environmental performance, individually and collectively. These Reviews are supported by a broad range of economic and environmental data. . .
click on photo to enlarge
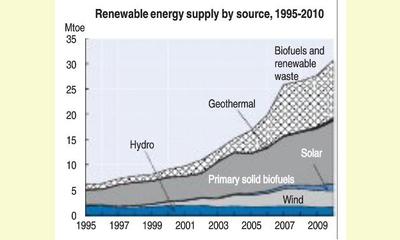
The use of renewable energy sources more than tripled in the last decade. In 2010, renewables accounted for 10% of primary energy supply and were the third largest source of electricity.
Biomass was the largest source of renewable fuel (40%), whereas wind was the largest source of renewable electricity (36%). Electricity generation from solar photovoltaics has dramatically increased since 2000, and it accounted for nearly 12% of electricity from renewables in 2010.
Renewable energy sources are expected to account for an increasingly large share of energy supply as Germany progressively phases out nuclear power by 2022. . .
Germany has made considerable progress in reducing the carbon and energy intensities of its economy. It is one of the few OECD countries that managed to absolutely decouple greehouse gas emissions (GHG) from economic growth in the 2000s. Domestic GHG emissions delined more than required by the Kyoto target. Energy efficiencey improvements and the rapid development of renewable energy sources were among the key drivers of this decline. However, Germany's energy and electricity mixes remain heavily dependent on fossil fuels, which results in slightly higher GHG emissions per unit of Gross Domestic Product than the average of OECD Europe.
|



|
DISCUSSION
Question(s) liée(s) à cet article:
Is there a future for nuclear energy?,
* * * * *
Commentaire le plus récent:
simple answer NO

|
|