. . WOMEN’S EQUALITY . .
An article from the United Nations
Following are UN Secretary-General António Guterres’ remarks to the Security Council annual open debate on women, peace and security, in New York today:
Thank you for inviting me to brief the Council on this vital issue. And for reminding us of the key contribution Bertha Lutz made to the UN Charter and to women’s rights.
Many of you here today will have visited the exhibition on display outside the United Nations building. You will have seen the images of the women who embody the agenda we are discussing — women who are fighting injustice, building peace, and taking their rightful place at the table. It is a snapshot of the immense contribution women are making to peace and security around the world and a testament to the power of women’s leadership.

The world must take note. And it must take inspiration. Because today, we are on a knife’s edge. Conflicts are raging. Tensions are rising. Coups are erupting. Authoritarianism is on the march. The nuclear threat has mushroomed. Climate chaos is inflaming security challenges. And mistrust is poisoning global politics — weakening our ability to respond.
The figures speak for themselves on the dire state of our world: military spending is at a record high; displacement due to violence, conflict and persecution is at a record high; and 50 per cent more women and girls are living in countries threatened by fighting than in 2017.
Where wars rage, women suffer, where authoritarianism and insecurity reign, women and girls’ rights are threatened. We see this around the world. In Sudan and Haiti — women and girls brutalized and terrorized by sexual violence. In Afghanistan — the denial of women’s basic rights is wrecking lives and depriving people of life-saving assistance. And women and girls fleeing Russia’s invasion of Ukraine are at risk of being preyed on by traffickers and abusers.
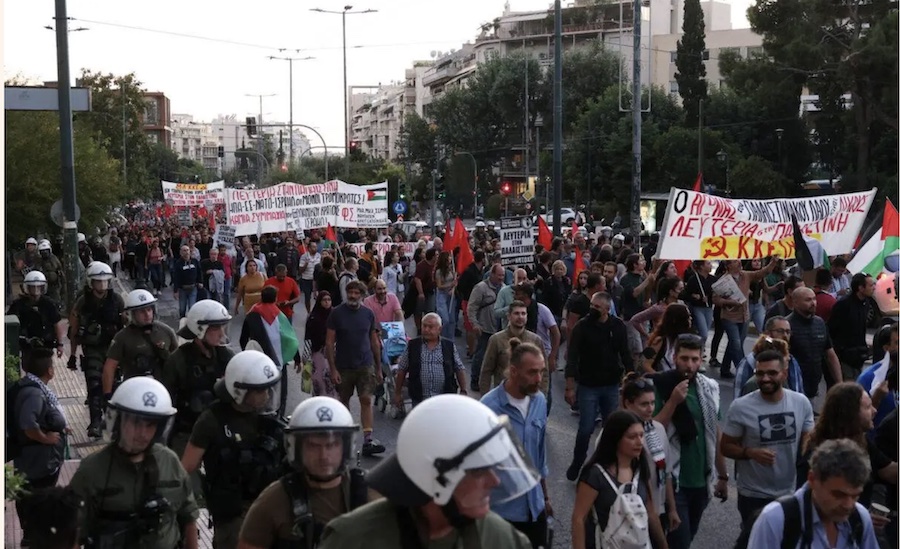
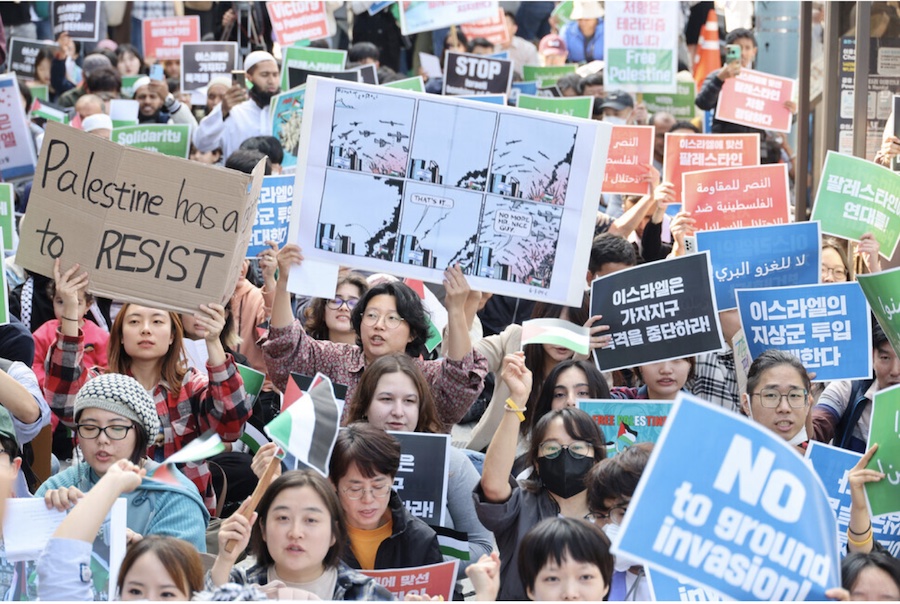
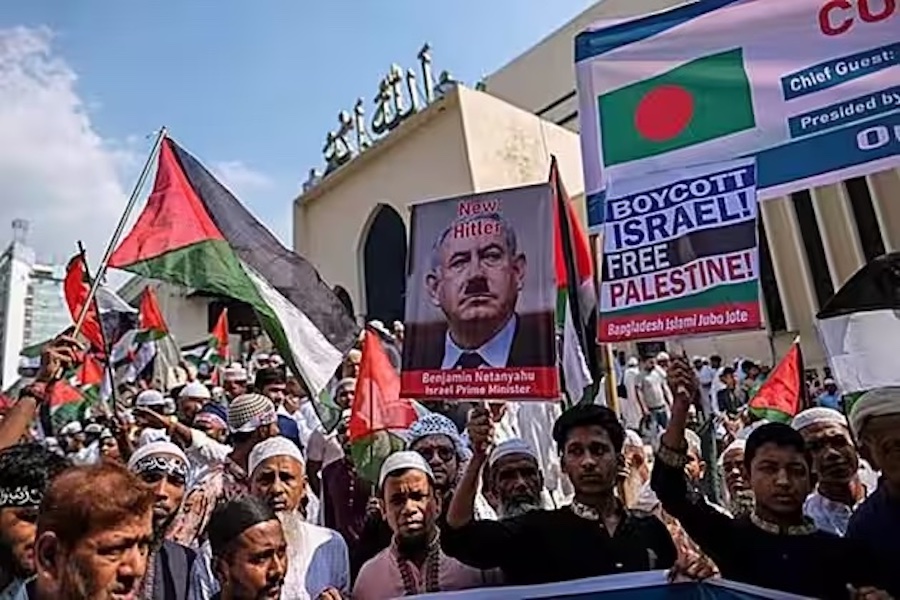
In the Middle East, women and girls are disproportionately affected by the ongoing violence, bloodshed and displacement. Women and girls are among the many victims of Hamas’ brutal atrocities. And women and children are more than half the victims of the relentless bombing of Gaza. Tens of thousands of pregnant women are desperately struggling to access essential health care.
This grim backdrop gives renewed urgency to efforts to ensure women’s full and meaningful participation in peace and security. Twenty-three years after this Council adopted resolution 1325 (2000), women’s participation should be a default, not an afterthought.
But that is not the case. Women are leading efforts on peace, justice and rights around the world. But still, far too many women’s organizations struggle to fund their essential work, as military spending soars; far too many perpetrators of sexual violence walk free; and far too many peace processes exclude women.
Of 18 peace agreements reached last year, only one was signed or witnessed by a representative of a women’s group or organization. Despite our best efforts, women represented just 16 per cent of negotiators or delegates in the peace processes led, or co-led, by the United Nations.
We live in a male-dominated world with a male-dominated culture. Centuries of patriarchy are a massive obstacle to gender equality and, in turn, to a culture of peace. Around the world, women’s rights are under attack. So are the people that defend them. At least seven women who briefed this Council last year report facing reprisals for having done so.
(Article continues in right column.)
Questions related to this article:
UN Resolution 1325, does it make a difference?
Does the UN advance equality for women?
(Article continued from left column.)
Violence against women — both on and offline — is endemic; a massive barrier and disincentive to participation in civil and political life. At the current rate of progress, it will be almost another half century before women are fairly represented in national parliaments.
Addressing this is not a favour to women. It is a matter of rights, justice and pragmatism. Standing with women is good for the world. We know processes involving women lead to more enduring peace. We know gender-equal parliaments are more likely to increase spending on health, education and social protection, and reduce corruption.
There are pockets of hope. This year’s report shows good practice and success stories on the women, peace and security agenda from around the world: from gender parity in Colombia’s peace negotiations to perpetrators of sexual violence in Iraq, Syria and the Central African Republic being brought to justice.
The United Nations is committed to working with countries to drive progress on women, peace and security. Our operations are supporting women, highlighting their vital work, and amplifying their voices. The Women’s Peace and Humanitarian Fund of the United Nations has supported more than 1,000 local women’s organizations since it was established in 2016. And we’ve made progress towards gender balance within peacekeeping missions. But overall, when it comes to women peace and security, the world must urgently bridge the gap between rhetoric and reality.
This annual debate regularly has the longest speakers’ list of the year. But concrete progress is slow, stagnant or even going backwards. We need to implement the women, peace and security agenda in full, now. Because women have had enough of being shut out of the decisions that shape their lives; enough of their work going unrecognized; enough of threats and violence; [and] enough of promises left unfulfilled. Women demand concrete actions to make real strides forward.
First, that means steps to ensure women are in the room for peace talks. I encourage Governments supporting conflict mediation to set ambitious targets for women on negotiating teams.
Second, it means money on the table. If you want to stand with women driving change, if you want to support women enduring conflict, if you want to remove barriers to participation, and if you want women’s organizations to deliver, we need to pay for it. Yet, the latest figures show aid funding for gender equality in conflict falling. I urge countries providing overseas development assistance, or ODA, to allocate 15 per cent to gender equality. Fifteen per cent of funds for mediation work must support women’s participation.
I also call on countries providing ODA to allocate 1 per cent — at a bare minimum — to direct assistance to women’s organizations mobilizing for peace. By the end of 2025, the Women’s Peace and Humanitarian Fund Invest-in-Women campaign aims to raise $300 million. I urge you to throw yourselves behind this effort.
Third, we need concrete measure to secure women’s full, equal and meaningful participation at all levels of decision-making on peace and security, and all levels of political and civil life. That means pushing fair representation in national and local governments, cabinets and parliaments.
I was a prime minister and leader of a political party. I know quotas, targets and incentives work. We need robust, comprehensive legislation to tackle violence against women — both on and offline — and to put an end to impunity for perpetrators.
And we need to make the most of the Summit of the Future next year to push for progress on women, peace and security. The Summit is a chance to reform and revitalize multilateralism so that it meets the challenges of today. In preparation, the policy brief on “A New Agenda for Peace” puts women’s leadership and participation at the centre of decision-making. I urge you to consider its proposals carefully.
Amidst a world in chaos, the clock is ticking down to the twenty-fifth anniversary of resolution 1325 (2000). A quarter century is ample time to make progress. We need to translate the energy, commitment and focus in this room into change on the ground and money on the table. No more stalling, no more coasting, no more delays.
We need to back the change-makers whose images we proudly display outside this building, starting today. The state of the world demands it. And women and girls, rightly, expect nothing less. Thank you.